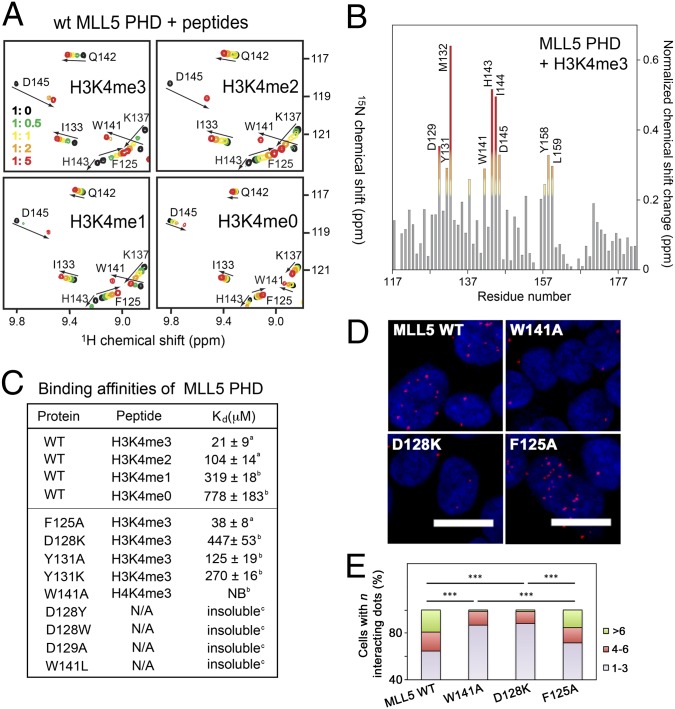
Fig. 3.
A unique H3K4me3 binding mechanism of MLL5 PHD. (A) Superimposed 1H,15N HSQC spectra of MLL5 PHD collected upon titration of indicated peptides. Spectra are color-coded according to the protein:peptide molar ratio. (B) The normalized chemical-shift changes observed in the PHD finger upon binding to H3K4me3 as a function of residue. (C) Binding affinities of WT and mutated MLL5 PHD for the indicated histone peptides measured by tryptophan fluorescence (a) or NMR (b). NB, no binding. (D and E) HEK293T cells expressing wild-type FLAG-MLL5 and mutants were fixed and stained with anti-FLAG and anti-H3K4me3 antibodies and with secondary antibodies conjugated with Duolink PLA probes and Duolink PLA detection reagents and imaged using a confocal microscope. Foci numbers in each cell were counted manually (400–500 cells were scored for each sample) and grouped into three categories: 1–3, 4–6, and >6. ***P < 0.001.