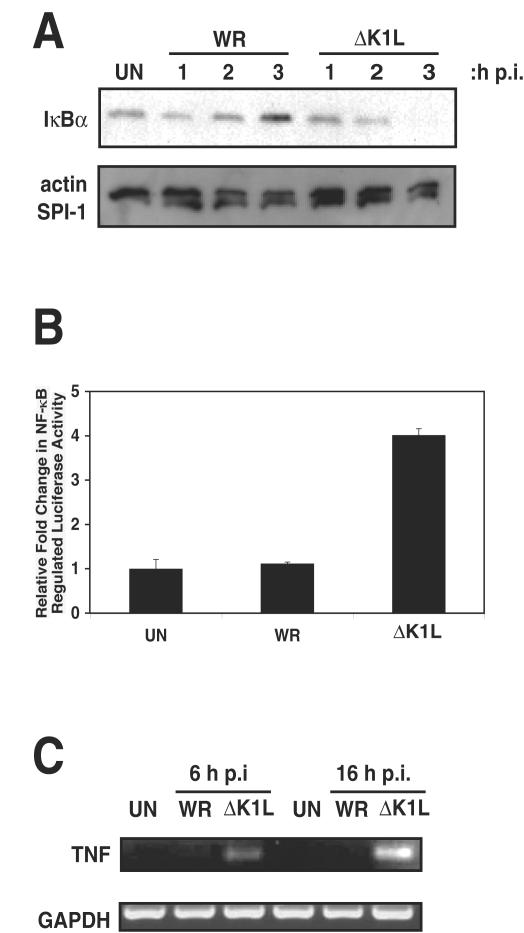
FIG. 4.
K1L is necessary for inhibition of NF-κB activation in RK13 cells. (A) RK13 cells were infected with WR or ΔK1L at an MOI of 10. At the times indicated postinfection, cells were collected and lysed in CE buffer. Equal amounts of cytoplasmic extracts were analyzed by using sodium dodecyl sulfate-12% polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis and subsequent Western immunoblotting with an IκBα antibody. In comparable blots, lysates were analyzed for actin levels to ensure equal protein loading and SPI-1 levels to ensure active virus infection. (B) RK13 cells were transfected with pRL-TK and pNF-κBluc, and 24 h posttransfection cells were infected (MOI = 10) with WR or ΔK1L. At 8 h postinfection, cells were lysed. The ratios of firefly to sea pansy activities were determined and normalized to that of uninfected cells. (C) RK13 cells were infected with WR or ΔK1L (MOI = 10). At 6 or 16 h postinfection, total RNA was isolated and mRNA was reverse transcribed into cDNA. TNF and GAPDH cDNAs were amplified by using PCR, and the resultant DNA products were separated by electrophoresis on a 2% agarose gel and visualized with ethidium bromide.