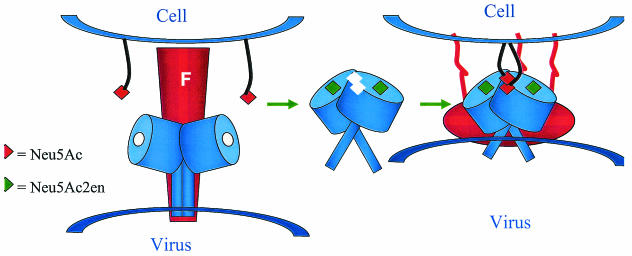
FIG. 6.
Model for fusion. (Left) F and HN hold each other in the switched-off state, with the region from 124 to 151 binding to the membrane-proximal HR2a region of F (18). HN binds to sialic acid receptors. (Middle) The sialic acid is released from the sialic acid-containing receptor, Neu5Ac2en is bound at the active site, the dimer association changes, and a new sialic acid binding site is created (F was removed for clarity). (Right) The changes in HN promote F into its fusogenic state, releasing its fusion peptide into the cell membrane while the virus is held proximal to the membrane by the sialic acid binding site. The structure(s) adopted by the HN stalk region is unknown.