Fig. 3.
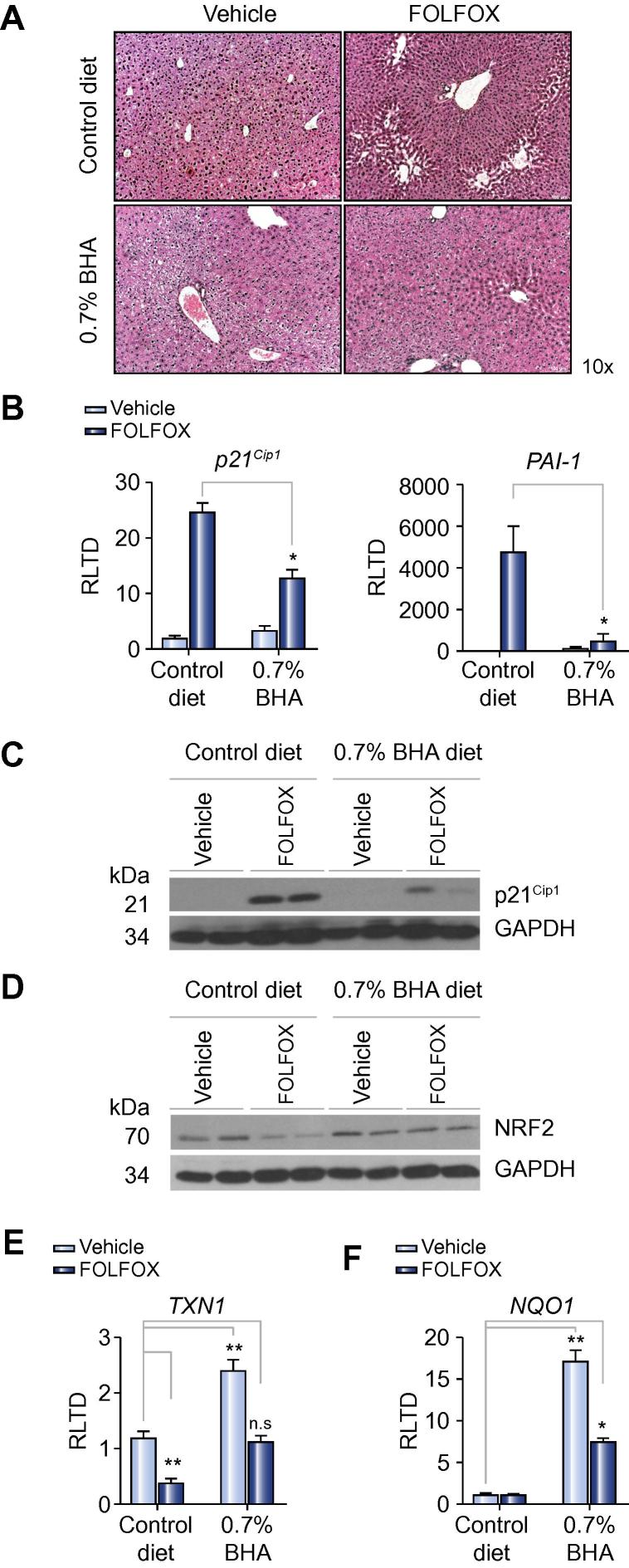
Oxidative stress in FOLFOX induced SOS. (A) To assess the role of oxidative stress in the development of SOS, the experiment was repeated, but this time supplementing the diet with 0.7% BHA with the purified diet serving as a control. Supplementation with 0.7% BHA prevented the development of sinusoidal injury. (B) In keeping with this, there was decreased expression of p21Cip1 and PAI-1 transcript (n = 5 per group, n = 4 in the FOLFOX and BHA group) in the livers of these animals. (C) The reduction in p21 expression was confirmed at a protein level by Western blot (representative blot of n = 2 per group). (D) FOLFOX induced SOS is associated with diminished expression of the antioxidant transcription factor NRF2 which is prevented when BHA is administered (representative blot of n = 2 per group). (E) BHA supplementation is associated with increased expression of the NRF2-regulated antioxidant genes TXN1 and NQO1 (n = 5 per group, n = 4 in the FOLFOX and BHA group). ∗p <0.05; ∗∗p <0.01; n.s, not significant. (This figure appears in colour on the web.)