Fig. 2.
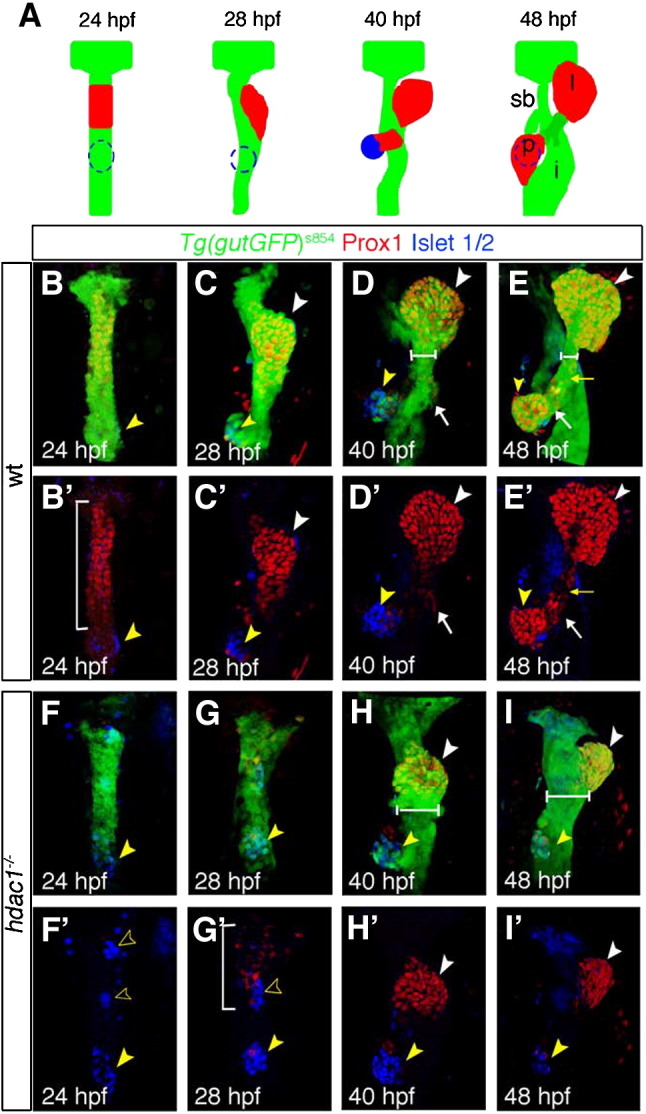
Specific requirements for Hdac1 in hepatic and pancreatic development. (A) Schematic depicting stages of endodermal organogenesis in wild type. Endoderm in green, Prox1-positive liver and exocrine pancreas in red, and endocrine pancreas in blue. l, liver; p, pancreas; dotted line, endocrine pancreas; sb, swim bladder; and i, intestinal bulb. (B–I′) Time course analysis comparing endodermal organogenesis of wild type siblings and hdac1 mutants, using the Tg(gutGFP)s854 line stained for Prox1(red) and Islet 1/2 (blue). Projection of confocal stacks showing ventral views of the Tg(gutGFP)s854 line expressing GFP throughout the endoderm (green), anterior to top. (B–E′), Wild type siblings, (F–I′), hdac1 mutants. (B, B′) At 24 hpf Prox1-expressing hepatoblasts are present throughout the organ-forming region of the endodermal rod (bracket). The endocrine pancreatic islet, stained with Islet 1/2, is situated posteriorly in the organ-forming region (yellow arrowhead). (C, C′) By 28 hpf the Prox1-positive hepatoblasts aggregate on the left side of the endodermal rod (white arrowhead) forming the liver bud. The exocrine pancreas expresses Prox1 at 40 hpf (arrow, D, D′) and 48 hpf; the liver and ventral pancreas are connected to the adjacent digestive tract by the extrahepatopancreatic duct (yellow arrow, E, E′). (F, F′) hdac1 mutants lack Prox1 expression at 24 hpf. The endocrine islet is present, although anterior groups of endocrine cells have formed (empty arrowheads). By 28 hpf, Prox1 expression is initiated in hepatoblasts (bracket, G, G′) which subsequently aggregate to form a medial liver bud by 40 hpf (white arrowhead, H, H′). By 48 hpf, in hdac1 mutants, the liver bud is located asymmetrically on the left side of the digestive tract (white arrowhead, I, I′). Exocrine pancreas and swim bladder fail to form at this time. Additionally, the width of the digestive tract is greater in hdac1 mutants than in wild type embryos once liver bud outgrowth has been initiated (compare horizontal bars, D, E with H, I).
