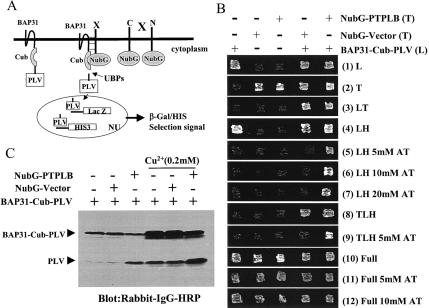
FIG. 1.
Identification of the BAP31-associated protein PTPLB in the novel split-ubiquitin yeast two-hybrid screen. (A) Diagrammatic representation of the split-ubiquitin two-hybrid system. Polypeptides that interact with the bait protein bring together the C-terminal fragment (Cub) and a modified N-terminal fragment (NubG, isoleucine 13 replaced by glycine) of ubiquitin, allowing ubiquitin-specific proteases (UBPs) to liberate PLV (protein A, LexA, and VP16) from Cub, which then is free to enter the nucleus (NU) and activate transcription of the lacZ and HIS3 reporter genes. (B) Growth of yeast L40 cells expressing BAP31-Cub-PLV, NubG, or NubG-PTPLB fusion proteins alone or together on various selective agar plates. BAP31-Cub-PLV in a leucine selection vector was integrated at the Cup1 genetic site in L40 yeast cells (pRSB-L40). NubG and NubG-PTPLB were constructed into a 2μm plasmid with tryptophan selection and transfected into L40 or pRSB-L40 yeast cells. The yeast strains containing various constructs were inoculated on agar plates with different selections. All the agar plates contained 0.2 mM Cu2+ with or without 3-aminotriazole (AT). (C) Western blot analysis of yeast L40 cell lines expressing BAP31-Cub-PLV fusion protein with or without coexpression of the NubG or NubG-PTPLB vector in the presence or absence of added Cu2+. Cells were grown to the logarithmic phase in relative selection medium. Proteins were extracted and analyzed by Western blotting with rabbit immunoglobulin G (IgG)-horseradish peroxidase (HRP) conjugate. L, lysine; T, tryptophan; H, histidine; full, no selection.