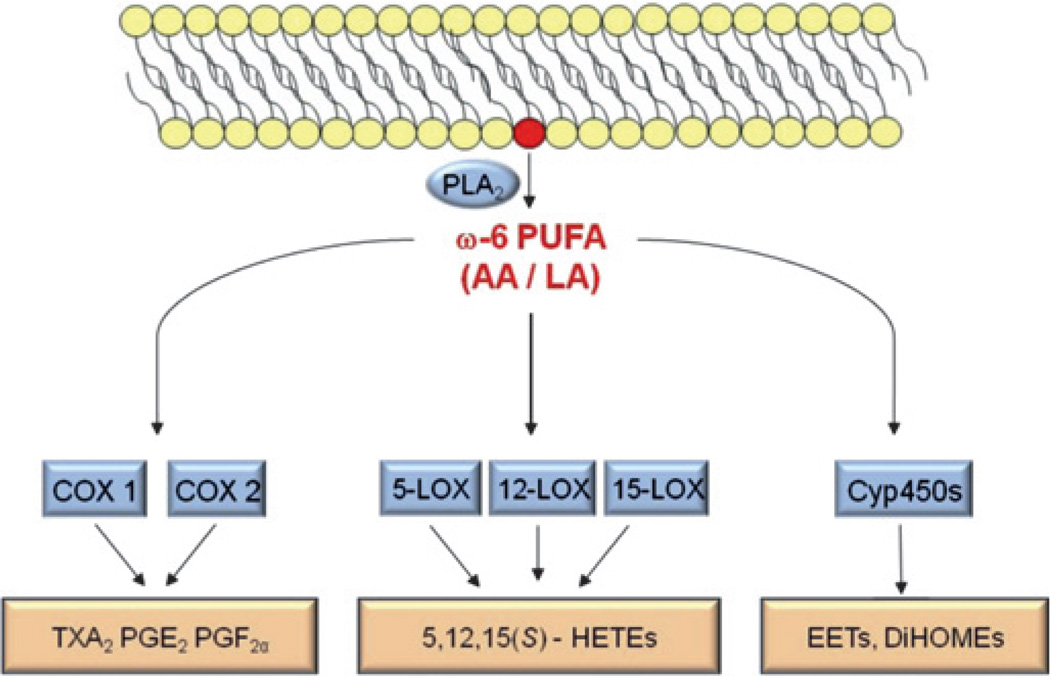
Figure 1.
Schematic of the major enzymatic pathways metabolising ω6-polyunsaturated fatty acids (PUFAs). Phospholipase A2 (PLA2) liberates ω6-PUFAs (eg, arachidonic acid (AA) or linoleic acid (LA)) from the cell membrane. These lipids are rapidly further metabolised by cyclooxygenase (COX), lipoxygenase (LOX) and cytochrome P450 (Cyp450) enzymes, generating the pathway-specific lipid metabolites thromboxane A2 (TXA2), prostaglandin (PG) E2, PGF2α, hydroxyeicosatetraenoic acids (HETEs), epoxyeicosatrienoic acids (EETs), dihydroxyeicosatrienoic acids (DiHOMEs) and others.