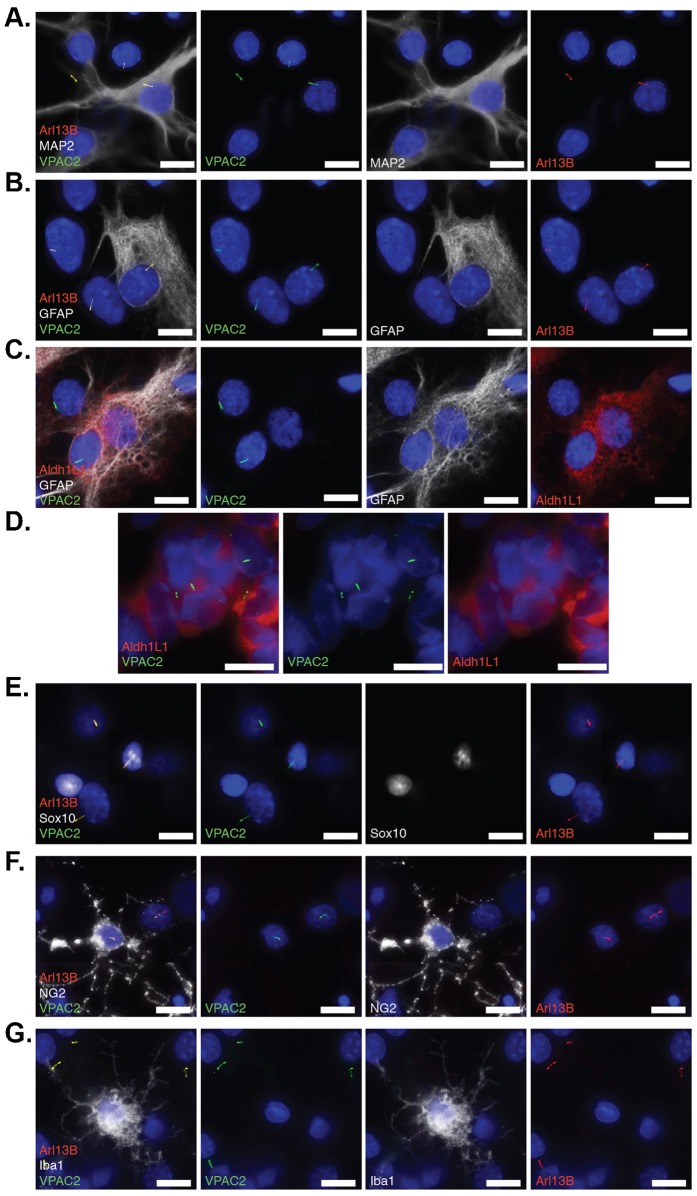
Fig. 3. Endogenous VPAC2 localizes to primary cilia of neurons and glial cells.
(A) VPAC2 localizes to primary cilia in neuronal (MAP2+) and non-neuronal (MAP2−) cilia in primary thalamic culture. Primary thalamic culture (DIV9) was immunostained for VPAC2 (green), MAP2 (white) and Arl13B (red). (B) VPAC2 localizes to primary cilia of astrocytes (GFAP+) in primary thalamic culture. Primary thalamic culture (DIV9) was immunostained for VPAC2 (green), GFAP (white), and Alr13B (red). (C) VPAC2 localizes to primary cilia of astrocytes (Aldh1L1+/GFAP+) in primary thalamic culture. Primary thalamic culture (DIV9) was immunostained for VPAC2 (green), GFAP (white), and Arl13B (red). (D) VPAC2 localizes to primary cilia of astrocytes (Aldh1L1+) in vivo. Brain cryosections from 7-day-old rat pups were fixed and immunostained for VPAC2 (green) and Aldh1L1 (red). (E,F) VPAC2 localizes to primary cilia of oligodendrocytes (Sox10+ or NG2+) in primary thalamic culture. Primary thalamic culture (DIV7) was immunostained for VPAC2 (green), Sox10 (white) and Arl13B (red) in panel E and VPAC2 (green), NG2 (white) and Arl13B (red) in panel F. (G) Microglial cells labeled with Iba1 do not possess VPAC2-positive cilia in primary thalamic culture. Primary thalamic culture (DIV7) was immunostained for VPAC2 (green), Iba1 (white) and Arl13B (red). (A–G) DNA was labeled with DAPI. Scale bars: 5 µm.