Figure 2. Simulation of MG (Metallic Glass) flow behavior using CFD (Computational Fluid Dynamics) method.
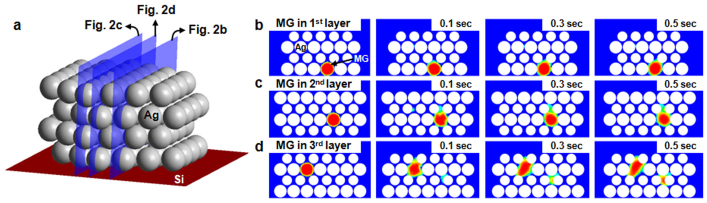
(a) Ag electrode model consists of MG and Ag particles on the Si substrate. Each of the three layers from the bottom contains one MG particle and 32 Ag particles, while the fourth layer has only Ag particles. Grey balls, dark red plate, and blue plates represent Ag particles, Si substrate, and cross section planes, respectively. MG volume fraction contour plots are shown at cross sections of the Ag electrode model where the MG particles are located in the (b) first, (c) second, and (d) third layer from the bottom. White balls represent Ag particles. MG volume fraction is displayed with the color ranging from blue (minimum value) to red (maximum value) on the contour plots. The MG particles begin to flow after 0.1 sec, and almost fill the gap between the Ag particles after 0.5 sec. Spontaneous flow of the MG occurs by the capillary effect due to the low contact angle (~ 20°) between MG-Ag and the low viscosity (~ 105 Pa·s) of the MG in its supercooled liquid region.
