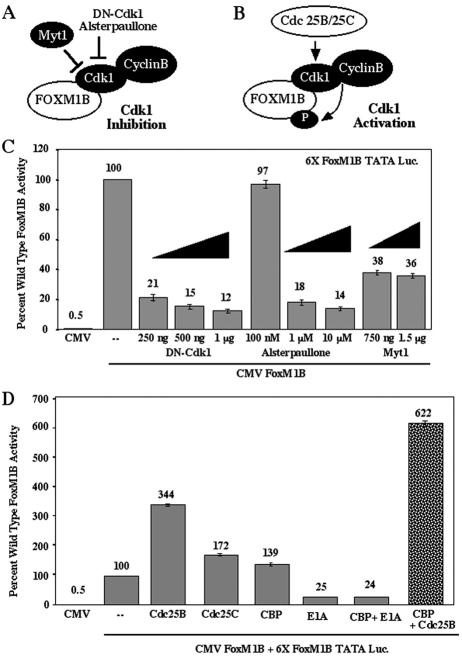
FIG. 5.
Inhibition of Cdk1 activity (DN-Cdk1 and Myt1) diminishes FoxM1B transcriptional activity, while stimulation of Cdk1 activity (Cdc25B and Cdc25C phosphatases) potentiates FoxM1B function. (A) Cartoon depicting inhibition of Cdk1 kinase activity by either Myt1 phosphorylation, dominant negative (DN) Cdk1, or the Cdk1 inhibitor Alsterpaullone. (B) Cartoon depicting stimulation of Cdk1 activity by Cdc25B and Cdc25C dephosphorylation. (C) Inhibition of Cdk1 activity diminishes FoxM1B transcriptional activity in cotransfection assays. U2OS-Tetr cells were transiently cotransfected with the reporter 6×-FoxM1B-TATA-luciferase or CMV-TO-FoxM1B (500 ng) alone or with increasing amounts of either CMV-DN-Cdk1, the Cdk1 pharmacological inhibitor alsterpaullone, or CMV-Myt1. FoxM1B expression was induced by tetracycline at 24 h following transfection, and pharmacological kinase inhibitors were added 5 h prior to FoxM1B induction. Cellular protein extracts were isolated at 48 h after transfection and assayed for dual luciferase activity. Results are expressed as a percentage of the activity with wild-type FoxM1B in four separate transfection experiments performed in triplicate to calculate standard deviations. (D) Activation of Cdk1 activity by dephosphorylation with either Cdc25B or Cdc25C stimulates FoxM1B transcriptional activity, which is potentiated by increased CBP levels. FoxM1B transcription assays in U2OS-Tetr cells were performed as described in the legend to Fig. 3C with either CMV-Cdc25B phosphatase or CMV-CBP either alone or in combination, demonstrating that increased Cdc25B levels enhanced CBP-mediated stimulation of FoxM1B transcriptional activity. Cotransfection assays with CMV-CBP and CMV-E1A, which inhibits the histone acetyltransferase activity of the CBP protein (9), eliminated CBP-mediated stimulation of FoxM1B transcriptional activity. Also shown is cotransfection with CMV-Cdc25C alone.