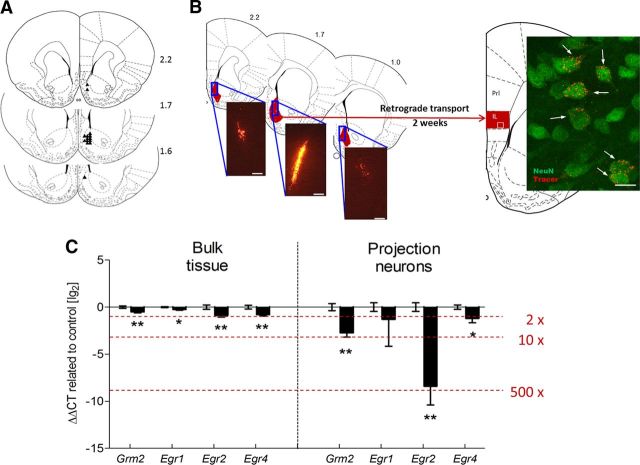
Figure 3.
Robust downregulation of Grm2 transcripts in rat infralimbic accumbens shell projection neurons lead to blunted response to Grm2 agonist treatment in postdependent (PD) rats. A, Locations of the 33 gauge injection cannula tips for the injections the retrograde tracer into the nucleus accumbens shell are represented by small black triangles. The cannula placements for the nucleus accumbens shell were verified within the region from +1.6 to +2.2 mm. B, Distribution of retrograde tracer within the nucleus accumbens shell (range, +2.2 to +1.0 mm relative to bregma). Fluorescent cells were clearly visible in sections from +1.9 to +2.5 mm relative to bregma in the infralimbic and the dorsal peduncular cortex. Insert shows a representative confocal microscope image. Arrows indicate retrograde tracer-positive cells, colabeled with the neuronal marker NeuN. Scale bars: left, 100 μm; right, 10 μm. C, Downregulated genes in glutamatergic projection neurons in the infralimbic cortex compared to the micropunched mPFC (bulk tissue) from the microarray study. The graph represents the delta delta cycle threshold ± SEM on a logarithmic scale of selected mRNAs, expressing the change in cycle thresholds from treatment to controls compared back to an endogenous control. In addition, Crym, a marker gene of glutamatergic pyramidal neurons according to the GENSAT mouse brain atlas (www.gensat.org), was highly expressed in all samples (quantitative PCR cycle threshold of ∼14), whereas Slc1a3, the gene for the glial glutamate transporter, was not detectable (cycle threshold, >39), indicating that we indeed succeeded in collecting a highly purified glutamatergic neuronal population. *p < 0.05; **p < 0.01. PreL, Prelimbic cortex; IL, infralimbic cortex.