Fig. 1.
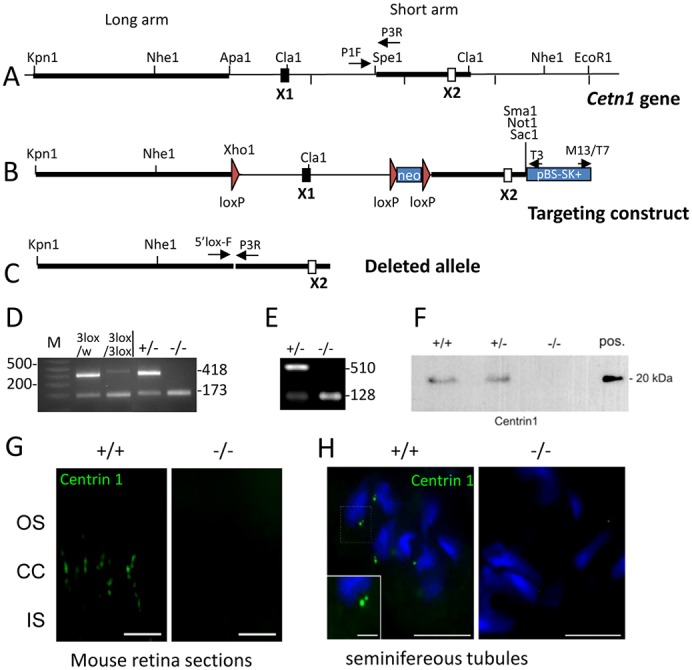
Cetn1 deletion. (A) The endogenous Cetn1 locus with one coding exon (X1) and one non-coding exon (X2). Long arm, short arm, loxP sites (red triangles) and relevant enzyme restriction sites are indicated. (B) The 3loxP knock-in construct with loxP sites flanking exon1 and neo for eventual deletion. (C) The deleted Cetn1 gene. (D) Genotyping of Cetn1loxP/WT;iCre75+ (labeled 3lox/w) and of Cetn13loxP/3loxP;iCre75+ mice (labeled 3lox/3lox), and Cetn1+/− and Cetn1−/− mice with retina DNA as PCR template. PCR amplification detects a wild-type allele at 418 bp in Cetn1+/− and a deletion product at 173 bp in Cetn1−/− mice. (E) RT-PCR was performed on extracts from Cetn1+/− and Cetn1−/− testes; 510 bp amplicons were detected for Cetn1+/− but not for Cetn1−/−. (F) Immunoblot of wild-type and Cetn1−/− testes protein extract. CETN1 is undetectable in the germline knockout mouse. (G) Immunohistochemistry of wild-type and Cetn1−/− retina cryosections using the anti-CETN1 antibody, MmC1. CETN1 localizes to wild-type photoreceptor cilia, but is undetectable in the Cetn1−/− retina. Scale bar: 10 µm. (H) CETN1 immunohistochemistry of wild-type seminifereous tubules. Antibody MmC1 detects characteristic dots (centrioles), one of which is brighter and bigger at the condensed nuclei in Cetn1+/+tubules, whereas in Cetn1−/− tubules, labeling is undetectable. Scale bars: 10 µm; inset, 5 µm.
