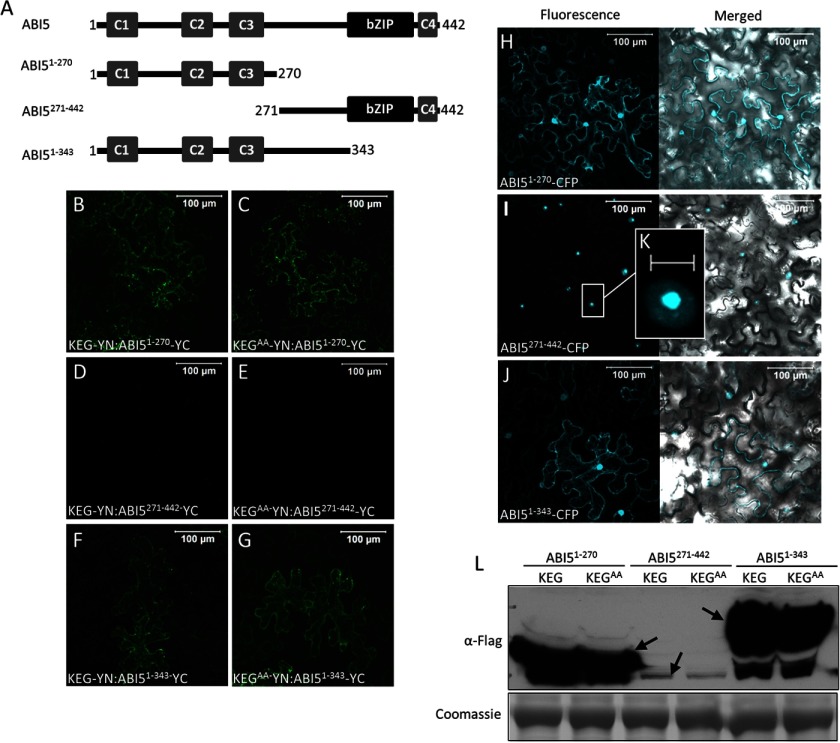
FIGURE 3.
C-terminal region of ABI5 regulates protein stability. A, schematic representation of ABI5 and ABI5 deletion mutants. Numbers indicate amino acids. B–G, BiFC analysis in tobacco epidermal cells. KEG-YN or KEGAA-YN was coexpressed with ABI51–270-YC (B and C), ABI5271–442-YC (D and E), or ABI51–343-YC (F and G). Bars = 100 μm. H–K, subcellular localizations of ABI51–270-CFP (H), ABI5271–442-CFP (I), and ABI51–343-CFP (J) in transiently transformed tobacco epidermal cells. Left panels show fluorescent images from a combined series of Z-stack. Right panels show transmitted light images overlaid with fluorescence images from a single optical section. Bars = 100 μm. K displays an enlargement of the section delimited by a white square in I. Bar = 10 μm. L, levels of ABI51–270-YC, ABI5271–442-YC, and ABI51–343-YC were determined following coexpression with KEG-YN or KEGAA-YN. Western blot analysis was done using protein extracts derived from the same tobacco leaf samples assayed for BiFC fluorescence shown in B–G. Note: ABI5-YC also contains a FLAG tag. Arrows indicate ABI5. Coomassie staining was used to confirm equal loading.