FIGURE 6.
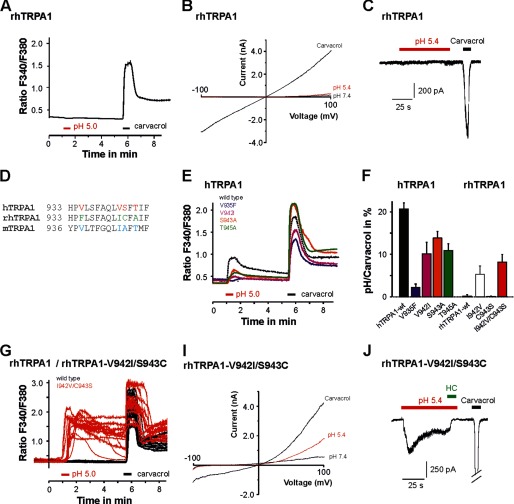
Specific residues within TM domains 5/6 dictate the effects of protons on hTRPA1 and rhTRPA1. A, calcium imaging on cells expressing wild-type rhTRPA1 challenged with pH 5.0 and 300 μm carvacrol. B, typical ramp currents elicited in the presence of pH 7.4, pH 5.4, and 300 μm carvacrol in cells expressing rhTRPA1. Currents were examined as described in Fig. 1. C, current trace on a cell expressing rhTRPA1 examined at −60 mV. Note that rhTRPA1 completely failed to respond to pH 5.4, whereas 300 μm carvacrol elicited large inward currents. D, alignment of TM domain 6 from hTRPA1, rhTRPA1, and mTRPA1. Non-identical amino acids are marked by colored letters. E, average calcium imaging responses of cells expressing the hTRPA1 wild type, hTRPA1-V935F, hTRPA1-V942I, hTRPA1-S943A, and hTRPA1-T945A or rhTRPA1-wild type, rhTRPA1-I942V, rhTRPA1-C943S, and rhTRPA1–942V/C943S. Cells were challenged by pH 5.0 and 300 μm carvacrol. F, proton-evoked responses of hTRPA1 mutant constructs, normalized to the response obtained by carvacrol. G, original calcium imaging traces on cells expressing the rhTRPA1 wild type (black) or rhTRPA1–942V/C943S (red), again challenged by protons and carvacrol as described in E. I, representative membrane currents of the mutant rhTRPA1-I942V/C943S, examined as described in Fig. 1. Note that this mutant produces outwardly rectifying current evoked by protons. J, representative proton-evoked (pH 5.4) inward currents in cells expressing wild-type rhTRPA1-I942V/C943S, rhTRPA1-I942V, and rhTRPA1-C943S. Recordings were performed in an extracellular solution containing 2 mm Ca2+. The inward current was blocked by coapplication of 100 μm HC030031 (HC).