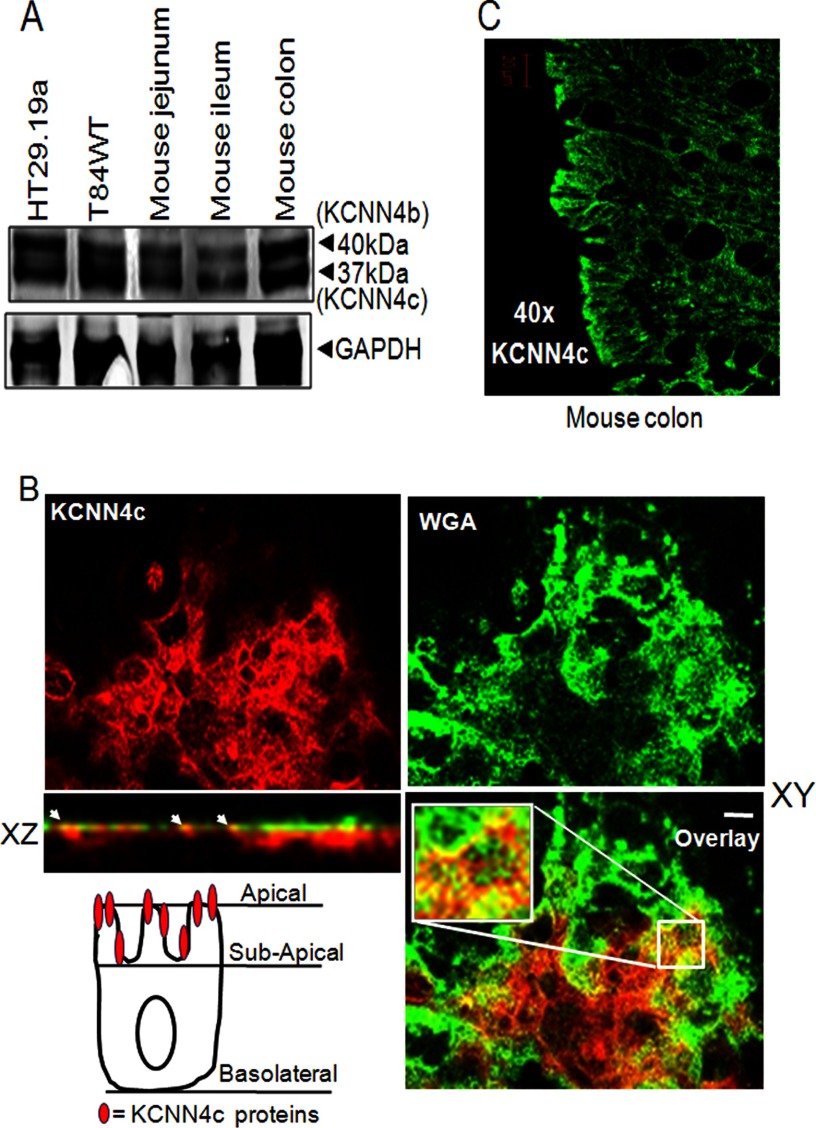
FIGURE 2.
Expression and polarization of KCNN4c on the apical membrane of intestinal epithelial cells and mouse intestine. A, proteins from total lysate of mouse intestinal tissues and human colonic cell lines were resolved by 10% SDS-PAGE as described under “Materials and Methods” and immunoblotted with KCNN4abc antibody. KCNN4 proteins migrate in all cases as two major bands with apparent molecular masses of 37 (KCNN4c) and 40 kDa (KCNN4b), respectively. B, colocalization of KCNN4c (red) with the apical membrane marker WGA (green) in T84WT cells. Polarized T84WT cells were grown on Transwell inserts and analyzed in xy and xz scans by confocal microscopy as described under “Materials and Methods.” The xy confocal section of T84WT cells shows clear apical membrane staining of KCNN4c colocalized with WGA. Colocalization is reflected by a yellow signal of the merged composite of xy and xz sections (bottom); the culture surface is at the bottom of image, and the apical surface of the cells is at the top. The merged image is shown in the bottom panel. Insets show enlarged regions within the white box. The xz plane of the region marked in the white square is shown at the bottom. Scale bars represent 10 μm. The cell illustration (bottom left) indicates the presence of functional KCNN4c on the apical most membrane but not beneath the subapical membrane in T84WT cells. C, KCNN4c in mouse colon. Paraffin sections of mouse colonic tissues were fixed and stained for KCNN4c (green), and xy images were collected by confocal microscopy as described under “Materials and Methods.” White arrows indicate colocalization hot spots.