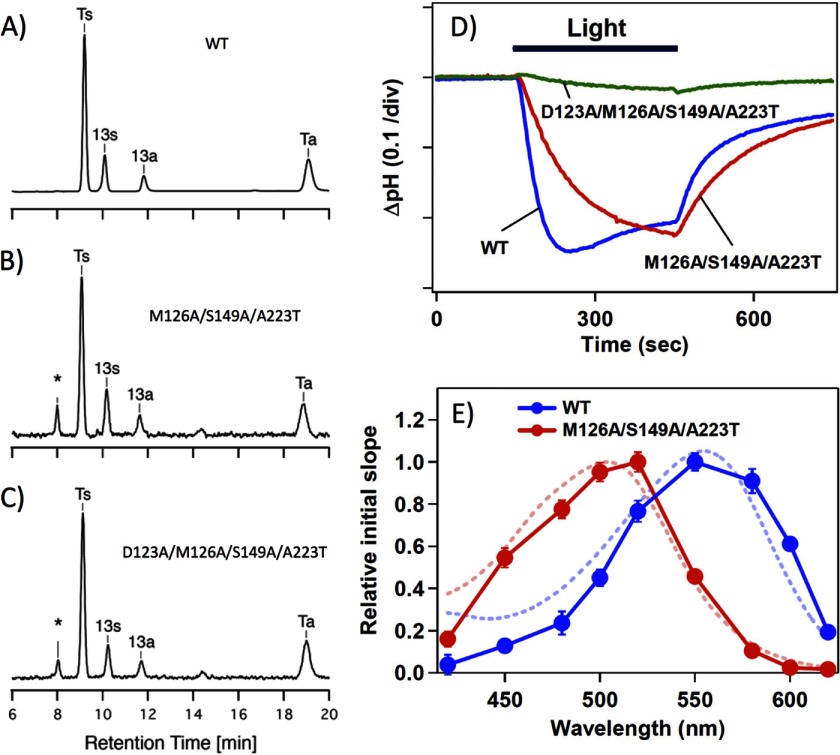
FIGURE 3.
Photochemical properties of the mutants. A–C, chromophore configurations extracted from the WT and the M126A/S149A/A223T and D123A/M126A/S149A/A223T mutants of HwBR. The detection beam was set to 360 nm. Ts, Ta, 13s, and 13a stand for the all-trans 15-syn retinal oxime, the all-trans 15-anti retinal oxime, the 13-cis 15-syn retinal oxime, and the 13-cis 15-anti retinal oxime, respectively. The molar composition of each retinal isomer was calculated from the areas of the peaks in the HPLC patterns, and the estimated molar compositions are listed in Table 1. D, light-driven pH changes in cell suspensions containing the WT (blue) or the M126A/S149A/A223T (red) or D123A/M126A/S149A/A223T (green) mutants of HwBR. Light indicates the illumination period (with yellow light, >500 nm for the WT and >460 nm for the mutants), and the negative signal corresponds to a decrease in pH (outward proton transport). One division of the vertical axis corresponds to 0.1 pH units. E, action spectra for the proton pumping activity in transformants containing the WT (blue circles) or the M126A/S149A/A223T mutant (red circles) of HwBR, which were estimated from the initial slopes of the pH change. The error bars indicate the standard deviations of three identical experiments. Blue and red dashed lines represent the absorption spectra of the light-adapted WT HwBR and M126A/S149A/A223T mutant, respectively.