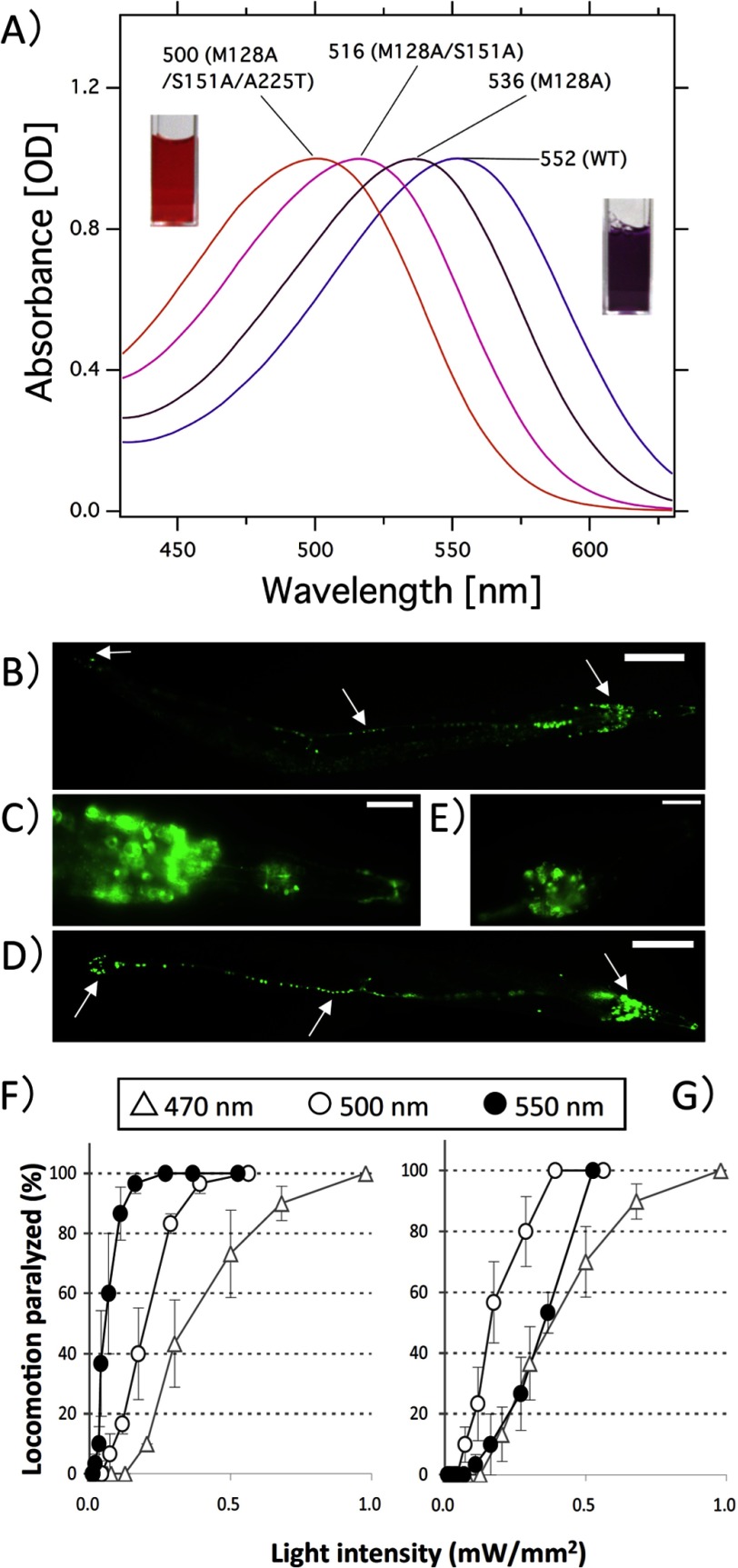
FIGURE 5.
Locomotion paralysis of C. elegans cells upon blue light illumination. A, visible absorption spectra of WT AR3 and its mutants. The spectra are scaled to be of similar intensity to the one of the WT by multiplying with 1.03 for M128A, 1.10 for M128A/S151A, and 1.08 for M128A/S151A/A225T, respectively. Met-128, Ser-151, and Ala-225 in AR3 correspond to Met-126, Ser-149, and Ala-223 in HwBR, respectively. The cuvettes colored orange and purple correspond to the purified M128A/S151A/A225T mutant of AR3 and the wild-type AR3, respectively. B and D, expression of WT AR3 (B) and the M128A/S151A/A225T mutant (D) of AR3 fused with GFP in C. elegans. GFP is expressed in the neurons (head neurons, tail neurons, and the ventral nerve cord) for both the WT and the mutant (arrow). C and E, expanded view. Scale bars, B and D = 100 μm; C and E = 10 μm. The anterior end is toward the right. F and G, dependence of the locomotion paralysis on light intensity. Animals expressing AR3::GFP were illuminated with different wavelengths of light (open triangles, 470 nm; open circles, 500 nm; closed circles, 550 nm) at varying light intensities for wild-type AR3 (F) and the M128A/S151A/A225T mutant (G). Error bars indicate ± S.E. Five animals were examined for each trial. We used the following three bandpass filters from Andover: 470 nm: FWHM = 10 nm; 500 nm: FWHM = 10 nm; 550 nm: FWHM = 10 nm.