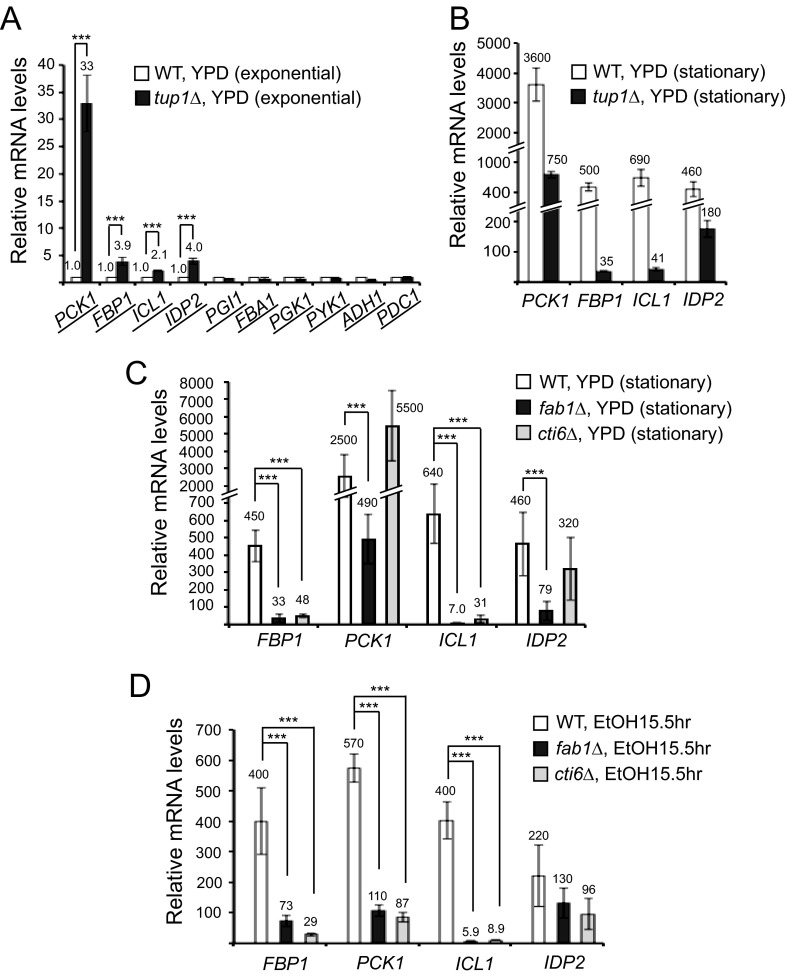
FIGURE 3.
CTI6 is required for transcriptional induction of ICL1 and FBP1. A, RT-qPCR analyses showed higher transcript levels of PCK1, FBP1, ICL1, and IDP2 in tup1Δ cells compared with the levels in WT cells (set as 1.0) in the exponential growth phase in YPD (n = 3). B, relative mRNA levels of PCK1, FBP1, ICL1, and IDP2 were analyzed by RT-qPCR in WT and tup1Δ cells in late stationary phase at 48 h in YPD compared with the levels in WT cells (set as 1.0) in the exponential phase in YPD (n = 3). C, relative mRNA levels of FBP1, PCK1, ICL1, and IDP2 were analyzed by RT-qPCR in WT, fab1Δ, and cti6Δ cells in late stationary phase at 48 h in YPD compared with the levels in WT cells (set as 1.0) in the exponential phase in YPD (n = 3). Transcriptional induction of FBP1 and ICL1, but not PCK1 and IDP2, was severely defective in cti6Δ cells at 48 h in YPD. D, relative mRNA levels of FBP1, PCK1, ICL1, and IDP2 were analyzed by RT-qPCR in WT, fab1Δ, and cti6Δ cells at 15.5 h after shifting from YPD to YPEtOH compared with the levels in WT cells (set as 1.0) in the exponential phase in YPD (n = 3). Transcriptional induction of FBP1, PCK1, and ICL1, but not IDP2, was severely defective in cti6Δ cells in ethanol medium. Error bars, S.D. ***, the two values of interest have a statistically significant difference with p values lower than 0.05.