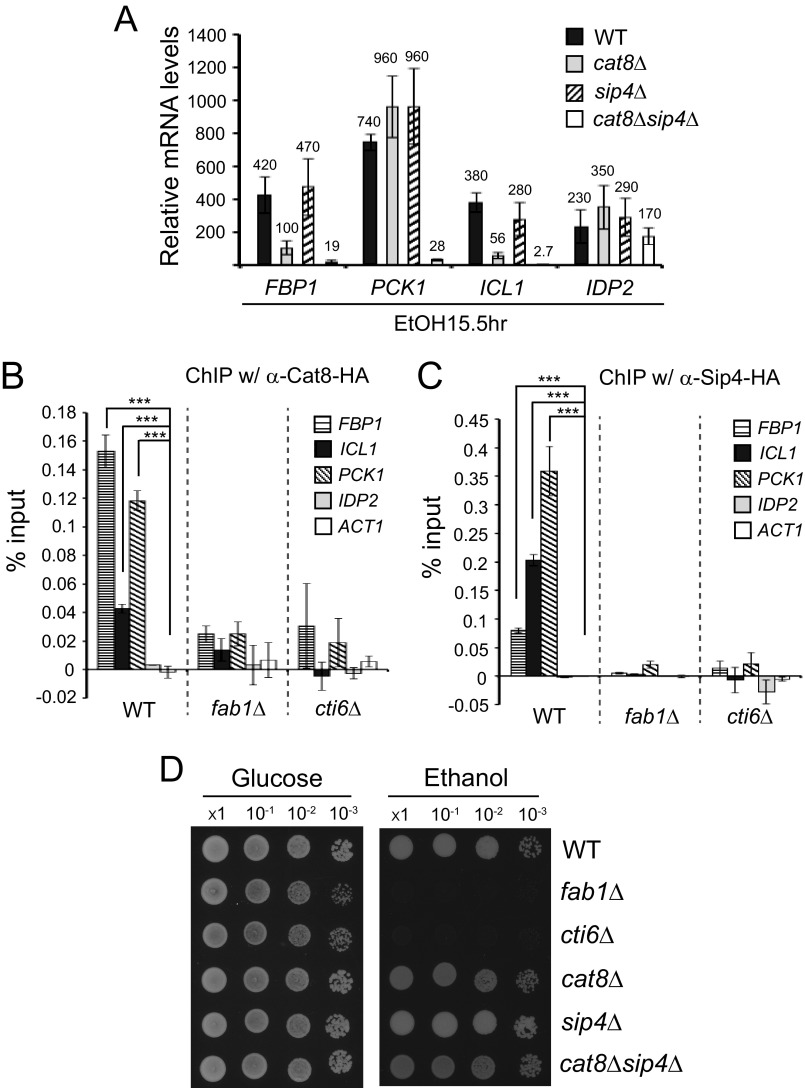
FIGURE 5.
The PIPTC is required for efficient recruitment of Cat8 and Sip4 activators to the gluconeogenesis gene promoters. A, relative mRNA levels of FBP1, PCK1, ICL1, and IDP2 were analyzed by RT-qPCR in WT, cat8Δ, sip4Δ, and cat8Δsip4Δ cells at 15.5 h after shifting from YPD to YPEtOH compared with the levels in WT cells (set as 1.0) in the exponential phase in YPD (n = 3). Error bars, S.D. Transcriptional induction of FBP1 and ICL1, but not PCK1 and IDP2, was significantly defective in cat8Δ cells. Deletion of SIP4 does not affect transcriptional induction of FBP1, PCK1, ICL1, and IDP2. Deletion of both CAT8 and SIP4 further reduced transcriptional induction of FBP1 and ICL1. Transcriptional induction of PCK1 was not affected in sip4Δ cells but was severely defective in cat8Δsip4Δ cells. Transcriptional induction of IDP2 was not significantly affected in either cat8Δ, sip4Δ, or cat8Δsip4Δ cells. B and C, ChIP-qPCR experiments were performed to analyze recruitment of Cat8 (B) and Sip4 (C) activators to the promoters of FBP1, ICL1, PCK1, and IDP2 in WT, fab1Δ, or cti6Δ cells grown in ethanol medium for 15.5 h after shift from YPD (n = 3). ACT1 promoter was analyzed as a negative control. Error bars, S.D. ***, the two values of interest have a statistically significant difference with p values lower than 0.05. D, the same numbers of cells in exponential growth phase in YPD were taken, washed, made in 10-fold serial dilution, and spotted on YPD and YP-ethanol media.