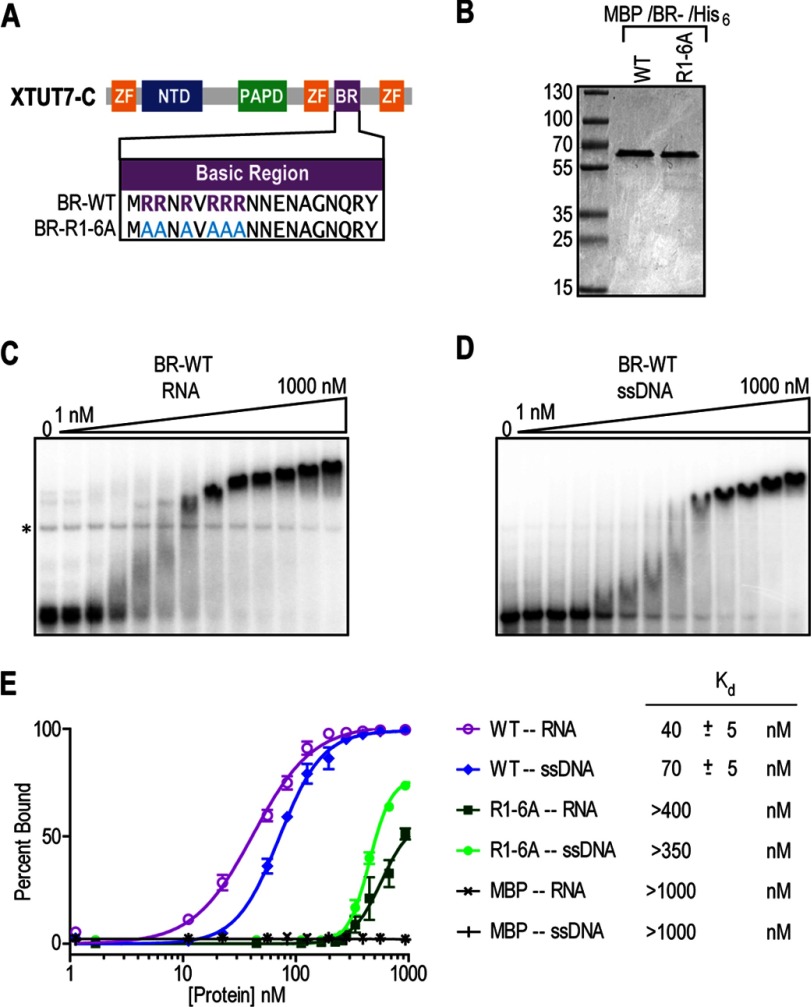
FIGURE 5.
The BR binds nucleic acids in vitro. A, diagram of the XTUT7 BR. MBP/BR/His6 fusion proteins were recombinantly expressed, purified, and tested by EMSAs. The R1–6A mutant protein was created by making the indicated amino acid substitutions in the BR. ZF, zinc finger domain. B, protein gel stained with Coomassie Blue. Molecular mass ladder (in kDa) (MW) is indicated. The expected molecular mass of the proteins was ∼57 kDa. C, EMSA using the wild-type BR fusion protein and a radiolabeled RNA containing three MS2-binding sites. Protein concentrations ranged from 1 nm to 1 μm, as indicated above the gels. The * indicates an RNA artifact that is present even in the absence of proteins. D, EMSA using the wild-type BR fusion protein and a radiolabeled ssDNA of equivalent sequence to the RNA substrate. Protein concentrations ranged from 1 nm to 1 μm, as indicated above the gels. E, the average percentage of nucleic acid substrate bound at each protein concentration was calculated and plotted using nonlinear regression analysis from three experiments. The apparent Kd values for fusion protein and nucleic acid substrate pairs are indicated to the right of the plot and reported with associated S.E.