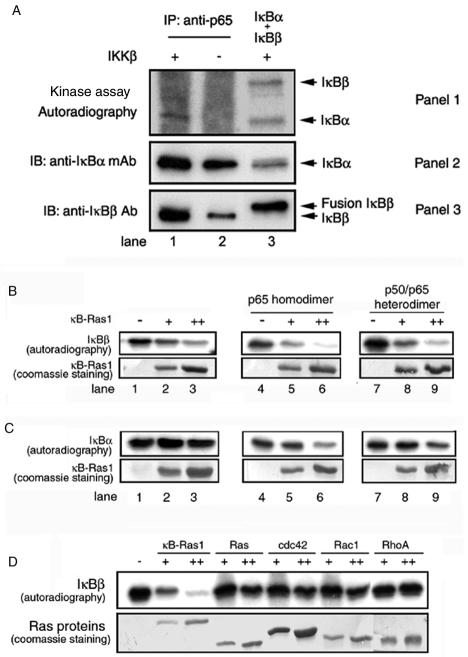
FIG. 2.
(A) Phosphorylation sites of IκBβ are blocked in vivo. IκB/p65 complexes were immunoprecipitated (IP) from the extract of 293 cells. Immunoprecipitated complexes were subjected to phosphorylation by pure (panel 1, lane 1) or mock (panels 1, lane 2) IKKβ. In parallel, a mixture of equimolar amounts of IκBα and IκBβ was subjected to phosphorylation by pure IKKβ (panel 1, lane 3). The reaction products were identified by separation of proteins by SDS-PAGE followed by autoradiography. The presence of IκBα and IκBβ in the immunoprecipitate or pure IκBα and IκBβ is shown by the Western blot (panels 2 and 3). Ab, antibody; mAb, monoclonal antibody; IB, immunoblotting. (B) Inhibition of IκBβ phosphorylation by κB-Ras in vitro. Pure IκBβ (1.5 μg) was subjected to phosphorylation by IKKβ, and the products were resolved by SDS-PAGE, transferred to membrane, and exposed to phosphorimaging. Phosphorylated IκBβ is shown in the absence (top panel, lane 1) or presence of 2 or 4 μg of pure κB-Ras1 (lanes 2 and 3). The effects of p65 homodimer (top panel, lanes 4 to 6) and p50/p65 heterodimer (top panel, lanes 7 to 9) on phosphorylation inhibition are shown in the absence (lanes 4 and 7) or the presence of κB-Ras1 (lanes 5 and 6 and 8 and 9). The bottom panel shows Coomassie staining of κB-Ras1 of the same blot used for the autoradiography. (C) Phosphorylation of IκBα by IKKβ. IκBα (top panel, lanes 1 to 3), IκBα/p65 complex (lanes 4 to 6), and IκBα/p50/p65 (lanes 7 to 9) were subjected to phosphorylation in the absence (top panel, lanes 1, 4, and 7) or presence (lanes 2 and 3, 5 and 6, and 8 and 9) of increasing amounts of κB-Ras. The bottom panel shows Coomassie staining of the same blot. Only the κB-Ras portion of the blot is shown. (D) Phosphorylations of IκBβ in the presence or absence of κB-Ras1, H-Ras, cdc42, Rac1, and RhoA (top panel). The bottom panel shows the Coomassie staining of the Ras proteins used in the reaction.