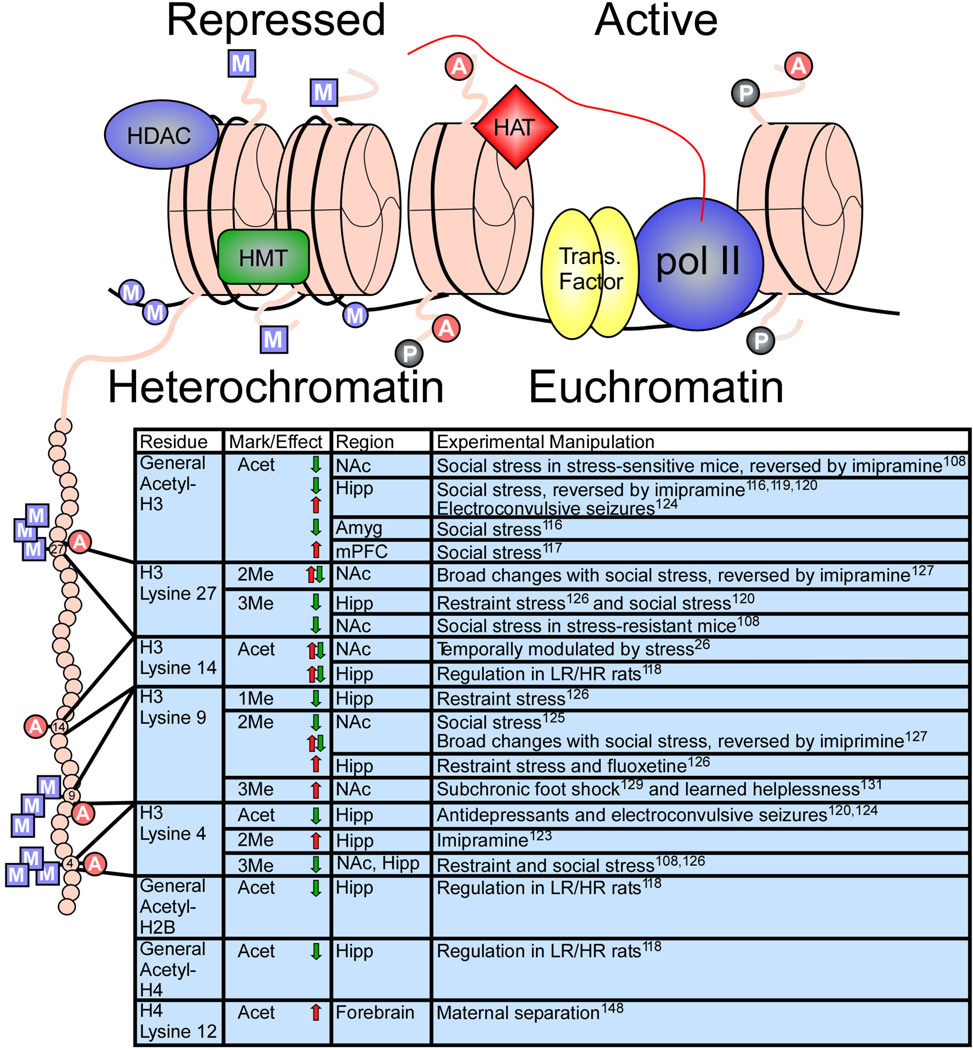
Figure 2. Chromatin modifications regulated by stress or antidepressant treatment.
Illustration (top) indicates histone octomers (pink) in heterochromatin (left) and euchromatin (right), along with associated proteins and histone tail/DNA modifications. A, acetylation; P, phosphorylation; square M, histone methylation; circle M, DNA methylation. Table (bottom) lists histone tail modifications of specific residues—depicted on the expanded histone tail illustration (left)—that are regulated by various stress paradigms or antidepressant treatments within the indicated brain regions. Arrows indicate an increase (red) or decrease (green) in specific modifications. References are in superscript. HDAC, histone deacetylase; HMT, histone methyltransferase; HAT, histone acetyltransferase; Pol II, RNA polymerase II; Trans. Factor, transcription factor.