Figure 5.
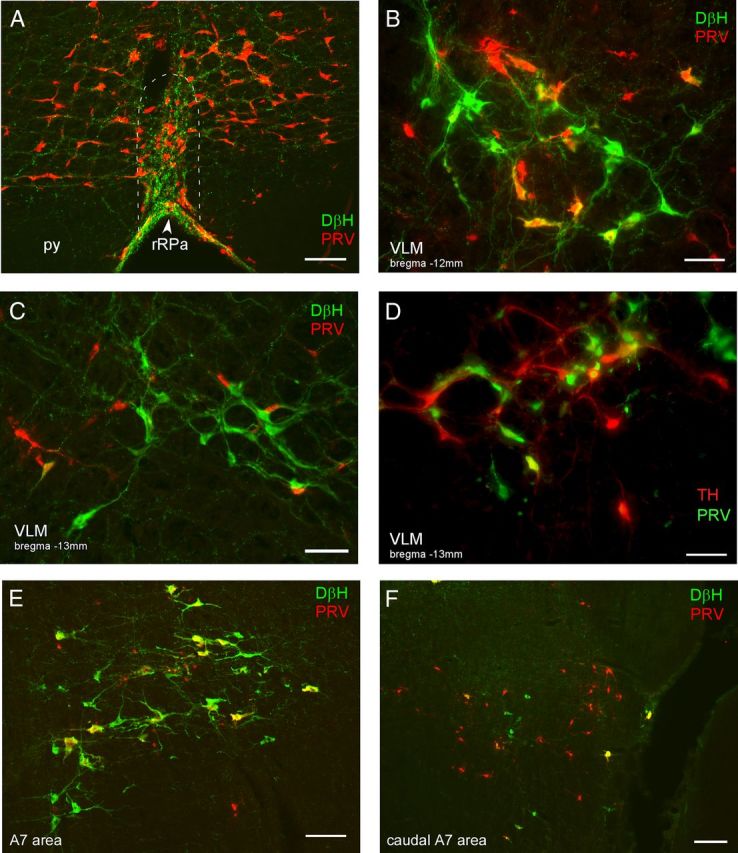
Neurons in the medulla and pons are synaptically connected to BAT. A–F, Photomicrographs are taken from rats that were killed 90 h (A–C, E) or 98 h (D, F) after injection of PRV into BAT. A, PRV-infected neurons (red) and DβH-ir fibers (green) in the rRPa (approximate boundaries indicated by the dashed white line), note the density of varicose DβH-ir fibers in close apposition to the PRV-ir neurons in the rRPa. py, Pyramidal tract. Photomicrographs illustrating PRV-ir (red), DβH-ir (green), and double-labeled (yellow) neurons in the VLM, ∼12.0 mm caudal to bregma (B) and 13.5 mm caudal to bregma (C). Note the double-labeled (yellow) neurons in the rostral VLM (B) but not the caudal VLM (C) at 90 h post-inoculation. D, Photomicrograph illustrating PRV-ir (green), TH-ir (red), and double-labeled (yellow) neurons in the VLM ∼13.3 mm caudal to bregma. Note that caudal VLM neurons become infected at long postinoculation times (98 h). E, A7 neurons of the rostral pons are infected at early postinoculation times, as illustrated by the double-labeled (DβH-ir, PRV-ir, yellow) neurons. F, At later postinoculation times, in the region of the pons containing the caudal aspect of the A7 population (DβH-ir, green neurons) there are many PRV-ir (red) neurons that are not DβH-ir. Scale bars: A, E, 100 μm; B, C, D, 50 μm; F, 200 μm.
