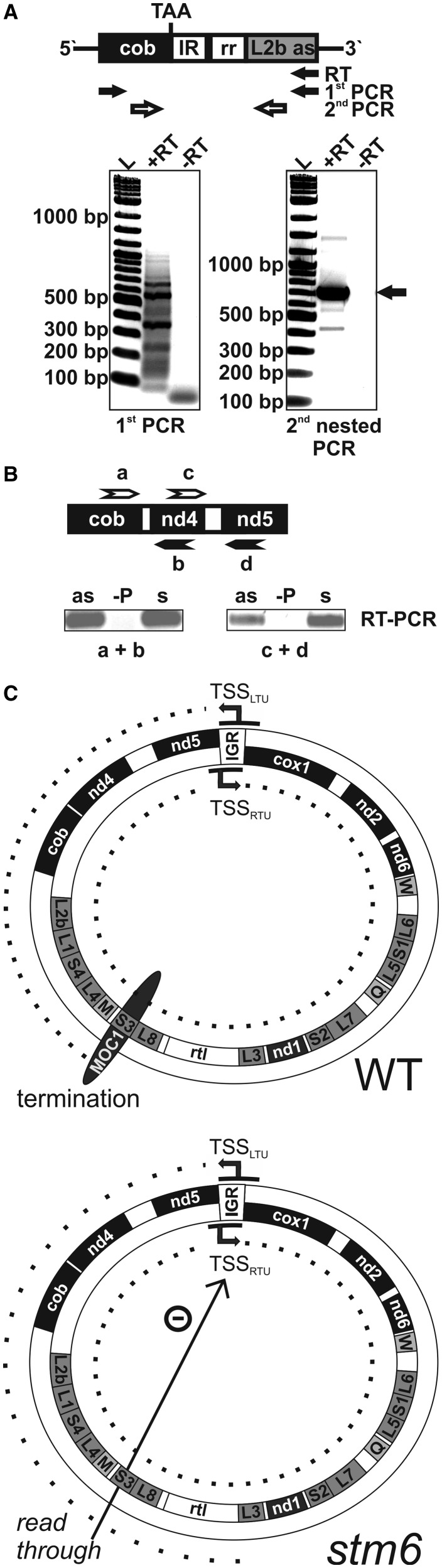
Figure 6.
Evidence for co-transcription of cob and L2b and a functional model for MOC1. (A) Upper panel: Structure of a transcript containing the coding sequence of cob and L2b in antisense (as) orientation, which results from the linkage of the left and right arm of the C. reinhardtii mitochondrial genome. The cob sequence and L2b as flank an inverted repeat region (IR) and the 86-bp region (rr) according to Vahrenholz et al. (4). TAA indicates the stop codon of the cob open reading frame. Detection of the transcript by RT–PCR involved RT with a gene-specific primer binding to the L2b as part of the transcript in the first step and two successive PCR reactions with nested primers (white arrows) used in the second PCR step. Lower panel: SYBR Gold stain of an agarose gel used to separate the PCR products of the first and second PCR reaction. Reverse transcription was carried in the absence (−RT) or presence (+RT) of reverse transcriptase. The main PCR product of the second PCR amplification (black arrow) was gel extracted and sub-cloned for sequencing. (B) Detection of antisense RNA derived from the non-coding strand of the left mtDNA arm by RT–PCR. RNA was converted to cDNA by strand-specific reverse transcription to detect antisense RNA (primers a and c; upper part) or sense RNA (primers b and d). PCR (primers a + b or c + d) was used to amplify cDNA before gel separation of products and staining (lower part). As a control, reverse transcription was performed in the absence of primers (−P). (C) A model depicting the function of MOC1 as it is suggested by the sum of data. Upper part: termination of LTU (left part of the circle) transcription by MOC1 at the S3-binding sites in a wild-type (WT) mitochondrion containing MOC1. The mtDNA of C. reinhardtii is presented as a circle. Black arrows indicate the direction of transcription, and dotted lines indicate the length of LTU/RTU-derived transcripts. Abbreviations: TSSLTU/RTU: transcription start sites of the leftward/rightward transcription units; IGR: intergenic region between nd5 and cox1; gene names as given in Figure 4A. Lower part: Lack of MOC1-mediated transcription termination in stm6. Read-through at the S3 site potentially reduces transcription of both units.