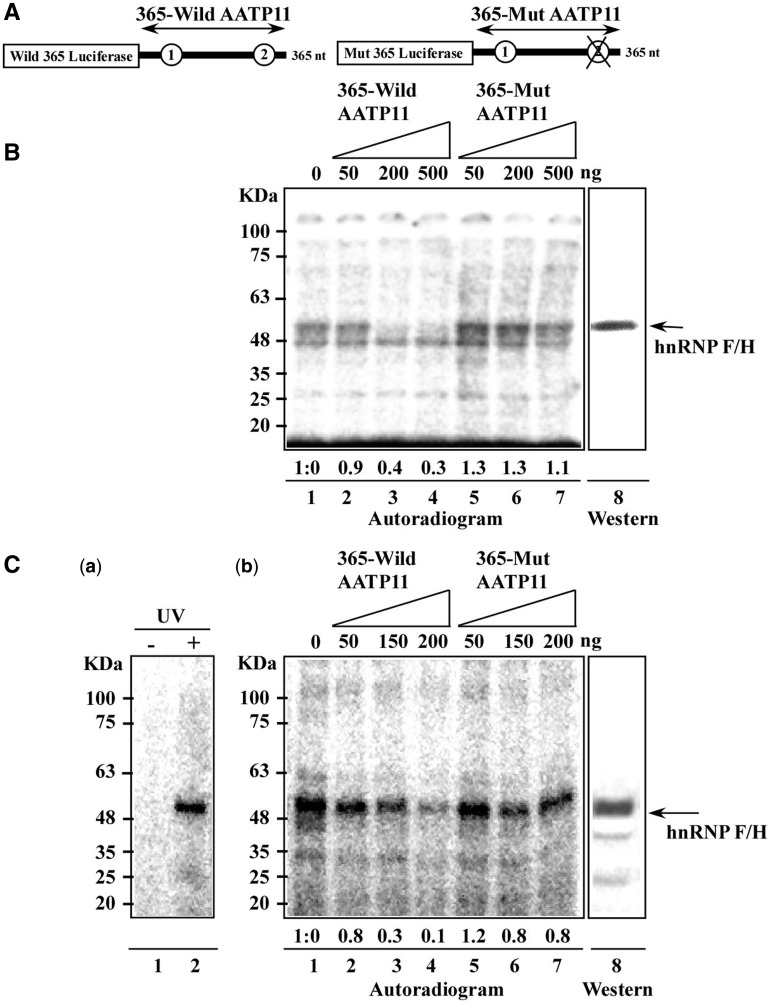
Figure 8.
HnRNP F/H protein is cross-linked to a transcript carrying the AAGAA site and to any RNA oligonucleotide coding for the two putative binding sites. (A) Schematic representation of the probes used for cross-linking. (B) Cross-linking using PCF extract. Cross-linking was performed as described in ‘Materials and Methods’ section, using whole cell extracts (15 µg per reaction) of PCF extract and in the presence of (lanes 1–4) increasing amounts of unlabelled 365-wild AATP11 transcripts (0, 50, 200 and 500 ng, respectively). Lanes 5–7 show increasing amounts of non-radioactive 365-mut AATP11 transcripts carrying the AAGAA mutation (50, 200 and 500 ng, respectively). Lane 8, a portion of the gel was subjected to western analysis with anti hnRNP F/H antibodies. The size of the protein marker is indicated. (C) Cross-linking using BSF extract. Extract (0.7 µg per lane) was cross-linked to the same substrates as in (B). (a) oligonucleotide (5′-AAGAAAAGAA-3′) (40 000 cpm) was end labelled at the 5′ end with [γ-32P]-ATP and was incubated with extracts in the absence (lane 1) or after UV irradiation (lane 2), (b). BSF extract (0.7 µg per lane) was cross-linked to (lanes 1–4) increasing amounts of unlabelled 365-wild AATP11 transcripts (0, 50, 150, and 200 ng, respectively). Lanes 5–7 show increasing amounts of non-radioactive 365-mut AATP11 transcripts carrying the AAGAA mutation (50, 150 and 200 ng, respectively). Lane 8, a portion of the gel was subjected to western analysis with anti hnRNP F/H antibodies.