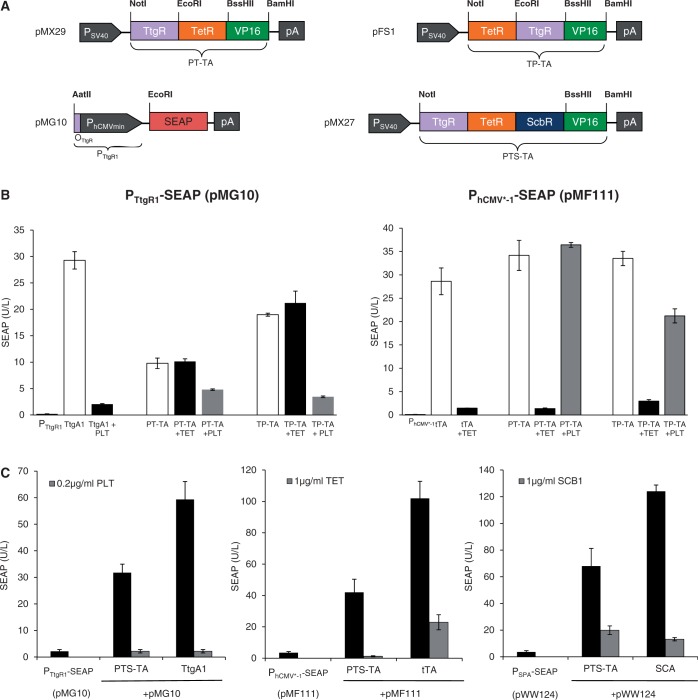
Figure 3.
Characterization of synthetic bi- and tri-partite TetR-family transactivators. (A) Bi- and tri-partite TetR-family repressor-derived mammalian transactivator variants assembled by fusing the TET-, phloretin- and γ-butyrolactone-dependent repressor proteins (TetR, TtgR, ScbR) to the Herpex simplex virus-derived transactivation domain (VP16). All multi-partite transactivator-encoding expression units are driven by the constitutive simian virus 40 promoter (PSV40) and contain a polyadenylation signal (pA). Corresponding target promoters contain specific operator sites (tetO7, OTtgR, OPapR1) immediately 5′ of a minimal version of the human cytomegalovirus immediate early promoter (PhCMVmin) and control expression of the human placental SEAP. (B) Regulation performance of the TtgR-TetR-VP16 (PT-TA) and TetR-TtgR-VP16 (TP-TA) transactivators. HEK-293T cells were co-transfected with PT-TA (pMX29) or TP-TA (pFS1) and either PhCMV*−1- (pMF111) or PTtgR1- (pMG10) driven SEAP expression vectors. Isogenic cultures expressing tTA (pSAM200) or TtgA1 (pMG11) instead of PT-TA (pMX29) or TP-TA (pFS1) were used as controls. Cells were grown for 48 h in the presence or absence of the trigger molecules TET (1 µg/ml) or phloretin (PLT, 0.2 µg/ml) before SEAP levels were scored in the culture supernatant. (C) Regulation performance of the tripartite TtgR-TetR-ScbR-VP16 transactivator (PTS-TA). HEK-293T cells were co-transfected with PTS-TA (pMX27) and either PhCMV*−1- (pMF111), PSPA- (pWW124) or PTtgR1- (pMG10) driven SEAP expression vectors. Isogenic cultures expressing tTA (pSAM200), SCA (pWW122) or TtgA1 (pMG11) instead of PTS-TA (pMX27) were used as controls. Cells were grown for 48 h in the presence or absence of the trigger molecules TET (1 µg/ml), γ-butyrolactone (SCB1, 1 µg/ml) or the phloretin (PLT, 0.2 µg/ml) before SEAP levels were profiled in the culture supernatant.