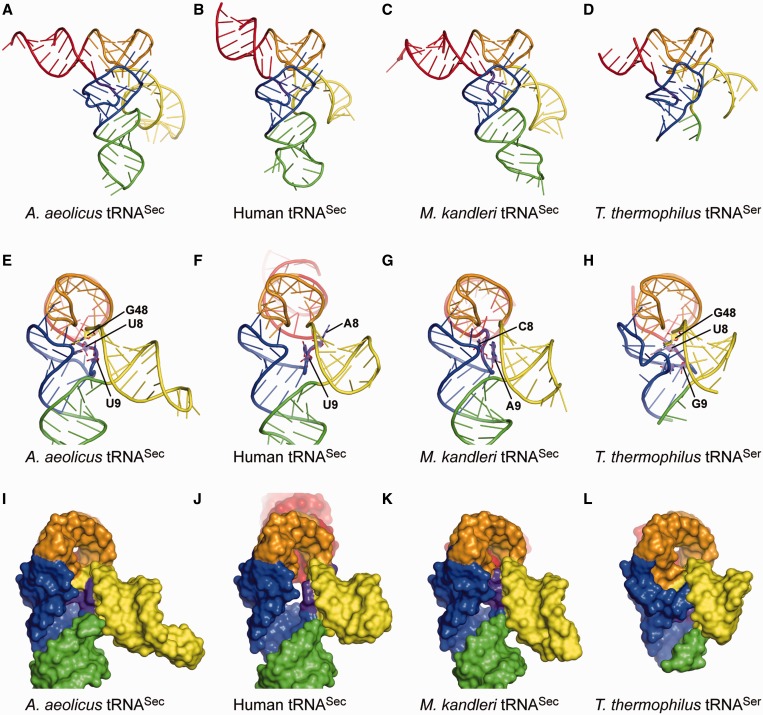
Figure 3.
Structure comparisons. (A–D) Overall views of the present A. aeolicus tRNASec (A), human tRNASec (B) [PDB ID: 3A3A (10)], M. kandleri tRNASec (C) [PDB ID: 3ADB (11)] and T. thermophilus tRNASer (D) [PDB ID: 1SER (9)] structures. The structures of M. kandleri tRNASec and T. thermophilus tRNASer are those in their complexes with PSTK and SerRS, respectively. The ribose-phosphate backbones and the bases are shown as tubes and ladders, respectively. Each arm is indicated in the same color as in Figure 1. G73 and the terminal CCA are disordered in the human tRNASec structure, while the distal portion of the acceptor arm, most of the anticodon arm and the extra-arm loop are disordered in the T. thermophilus tRNASer structure. (E–L) Side views of the ladder and surface models of A. aeolicus tRNASec (E and G), human tRNASec (F and J), M. kandleri tRNASec (G and K) and T. thermophilus tRNASer (H and L). The linker nucleotides at positions 8, 9 and 48 are shown as plate-stick models in (E–H). The eukaryal/archaeal tRNASecs lack the linker nucleotide corresponding to G48 in bacterial tRNASec. The orientation of the extra arm is similar among tRNASecs and tRNASer.