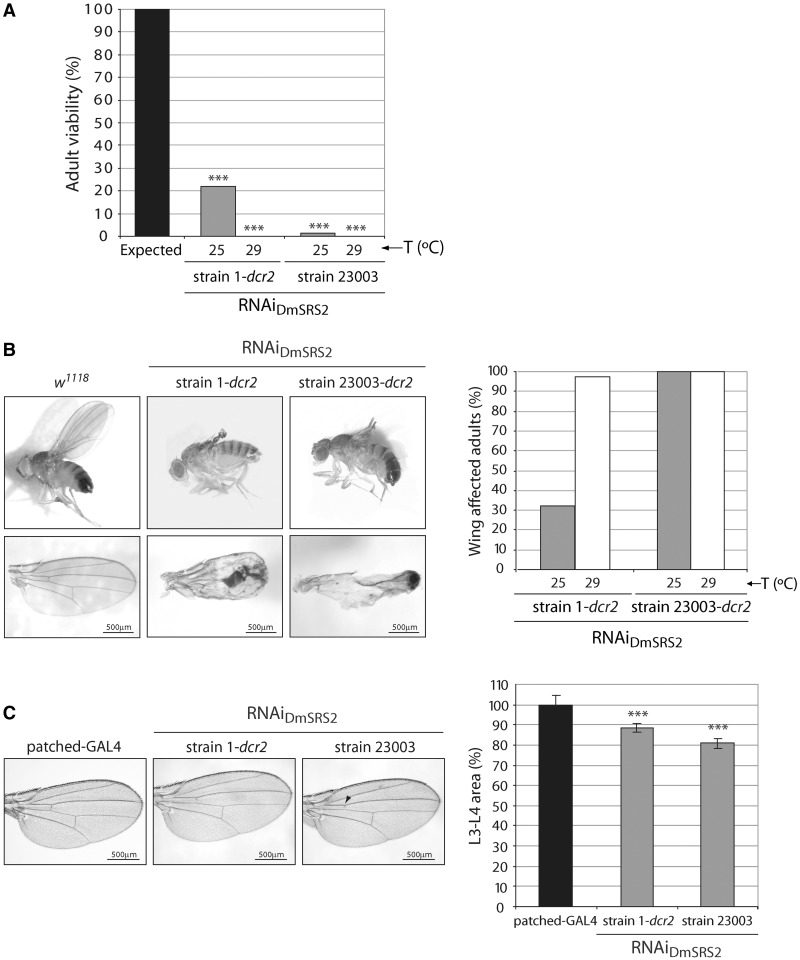
Figure 3.
In vivo effect of RNAi of DmSRS2. (A) Adult viability reduction caused by the constitutive and ubiquitous silencing of DmSRS2 at 25 and 29°C using the two RNAiDmSRS2 strains. Results are represented setting the maximum expected viability of RNAi active flies at 100%. Statistical significance is determined by Chi-square test (***P < 0.001). (B), DmSRS2 knockdown restricted to wing. The left panel shows images of adults from the crosses between nubbin-GAL4; UAS-dcr2 driver and RNAiDmSRS2 strain 1 and strain 23003, which suffer severe wing damage, and control flies (w1118). Scale bars correspond to 500 μm. Graph on the right represents the proportion of adults that exhibit wing defects when crosses are kept at 25 and 29°C. (C), Patched-GAL4 driver is crossed at 29°C with RNAi strains to restrict the DmSRS2 depletion in the region flanked by longitudinal veins L3 and L4. The images on the left show wings with a partial or total loss of the anterior cross vein (marked with an arrowhead) and a reduction in the L3-L4 area, compared with the parental line (patched-GAL4). Scale bars correspond to 500 μm. Graph on the right shows the averages with SEM of all the L3-L4 area measurements in percentage, compared with the parental line and statistics are performed by two-way ANOVA test (***P < 0.001).