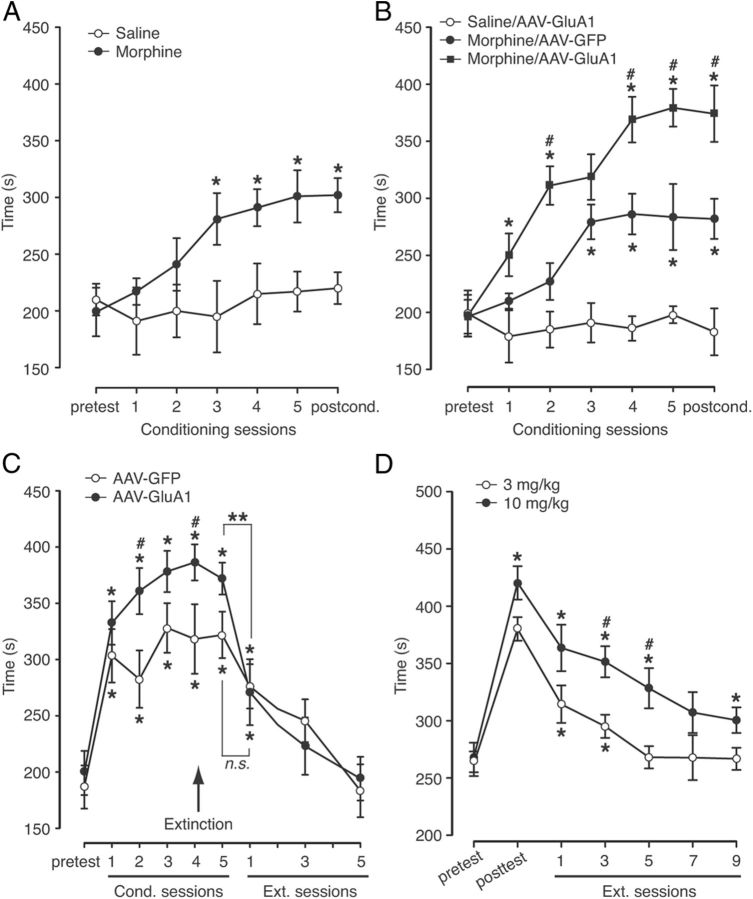
Figure 4.
Overexpression of CeA GluA1 subunits facilitates associative learning of morphine reward. A, Behaviors of CPP induced by multiple conditioning sessions with saline or a low dose of morphine (0.5 mg/kg, s.c.) (n = 6 rats/group). CPP tests were conducted after each number of sessions and after the completion of all conditioning sessions (postcond., postconditioning). *p < 0.05 (compared to the pretest in the same group). B, CPP behaviors after similar conditioning sessions with saline (n = 6) or morphine (0.5 mg/kg) in rats injected into CeA with AAV-GluA1 (n = 9) or AAV-GFP (n = 6). *p < 0.05 (compared to the pretest in the same group); #p < 0.05 (compared to the Morphine/AAV-GFP group). C, CPP behaviors in CeA AAV-GluA1- or AAV-GFP-injected rats conditioned with multiple sessions of morphine at 3 mg/kg, followed by daily conditioning sessions of extinction training with saline only (n = 9 rats/group). *p < 0.05 (compared to the pretest in the same group); #p < 0.05 (compared to the AAV-GFP group); **p < 0.01; n.s., not significant. D, CPP behaviors in normal rats (n = 8/group) induced by conditioning with morphine at 3 mg/kg and 10 mg/kg, followed by daily sessions of extinction training. *p < 0.05 (compared to the pretest in the same group); #p < 0.05 (compared to the 3 mg/kg group).