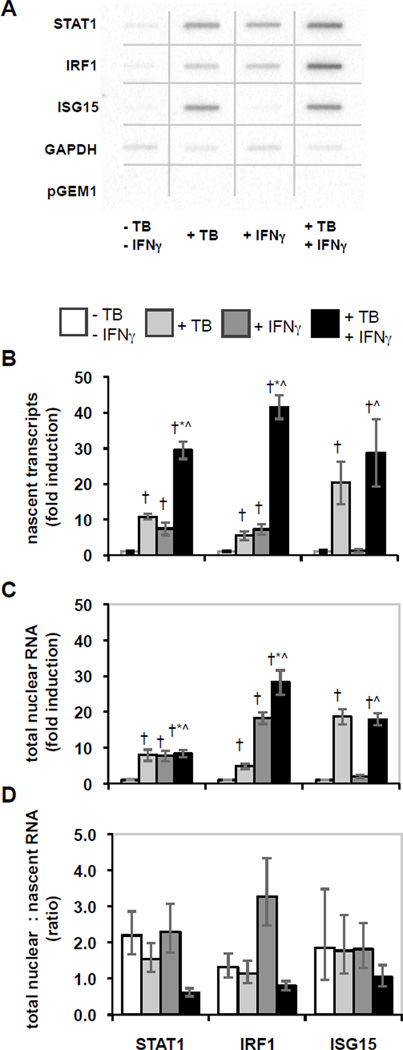
Figure 1.
Effects of M. tuberculosis infection and IFNγ stimulation on nascent and total nuclear RNA. THP-1 cells were differentiated, infected with M. tuberculosis and/or stimulated with IFNγ, and then nascent transcripts were measured using the nuclear run-on assay, or total nuclear RNA was extracted and quantified by qRT-PCR. A) The hybridization results for nuclear run-on assays were imaged and quantified using a phosphorimager. The figure is a composite of noncontiguous portions from a single phosphorimager exposure that included the membranes for all four conditions in a representative experiment. B) Nascent transcript measurement is shown as average fold induction ± SEM for 6 replicate experiments. Statistically significant differences (p < 0.05) are indicated compared to control (†), compared to M. tuberculosis (*), and compared to IFNγ (^). C) Total nuclear RNA abundance is shown as average fold induction ± SEM for 4–6 replicate experiments as for panel B. D) The ratios of the abundance of total nuclear RNA relative to the level of nascent transcripts were calculated from the averages for each. Error bars represent ± SEM.