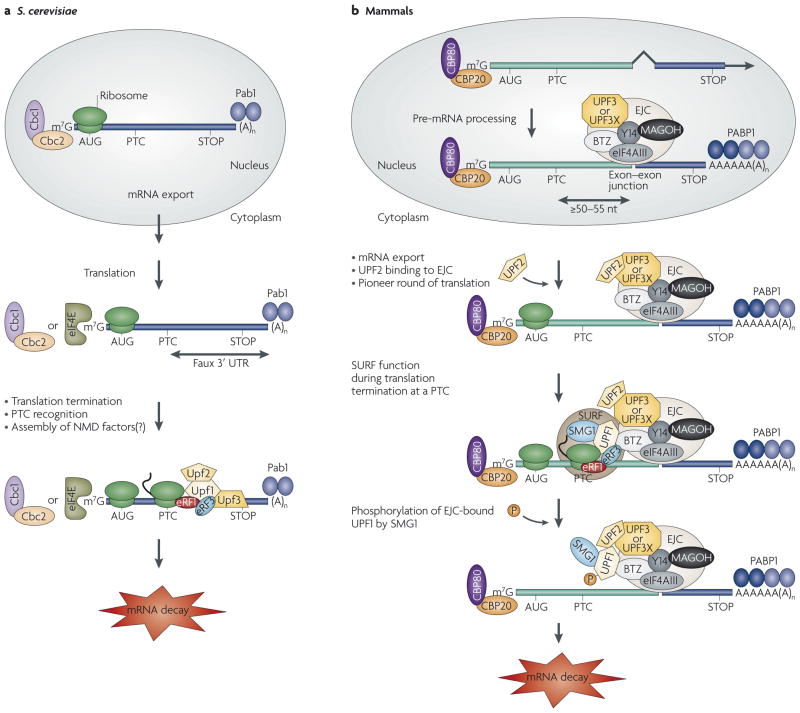
Figure 1. Models for nonsense-mediated mRNA decay in Saccharomyces cerevisiae and mammals.
a | In Saccharomyces cerevisiae, newly synthesized mRNAs that contain a premature termination codon (PTC) and that are bound to the RNA cap-binding protein heterodimer Cbc1–Cbc2 and to steady-state mRNAs that are bound by the cap-binding protein eukaryotic translation initiation factor 4E (eIF4E) are targeted for nonsense-mediated mRNA decay (NMD) once the mRNA is exported from the nucleus to the cytoplasm. In at least one mechanism, an abnormally long or ‘faux’ 3′ UTR results in inefficient translation termination. As a consequence, termination involves not only the eukaryotic release factor 1 (eRF1) and eRF3 translation-termination factors, which fail to effectively mediate the release of the nascent polypeptide because of an inefficient interaction between eRF3 and poly(A)-binding protein 1 (Pab1), but probably also the up-frameshift 1 (Upf1), Upf2 and Upf3 NMD factors. These factors then recruit and/or activate mRNA degradative activities. Although Upf1 is a phosphoprotein, whether Upf1 undergoes a cycle of phosphorylation and dephosphorylation during NMD in S. cerevisiae is unknown. b | In mammals, newly synthesized PTC-containing mRNA that is bound to the RNA cap-binding protein heterodimer CPB80–CBP20 is targeted for NMD once the mRNA has been generated by pre-mRNA splicing and exported from the nucleus to the cytoplasm. Notably, pre-mRNA splicing results in the deposition of an exon-junction complex (EJC) of proteins upstream of mRNA exon–exon junctions. Core EJC components consist of eIF4AIII, RNA-binding-motif protein Y14, mago nashi homologue (MAGOH) and Barentsz (BTZ; also known as cancer susceptibility candidate 3, CASC3). The UPF3 or UPF3X NMD factor, which shuttles to the nucleus, is thought to be recruited to EJCs in the nucleus and is exported with the mRNA to the cytoplasm. UPF3 or UPF3X then recruits UPF2, which is primarily cytoplasmic. The translation of mRNA that is bound to CBP80–CBP20 is termed the pioneer round. Translation termination at a PTC during the pioneer round involves the SURF complex, which consists of the phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase-related protein kinase (PIKK) SMG1 together with UPF1, eRF1 and eRF3. Generally, if translation terminates more than ~50–55 nucleotides (nt) upstream of an exon–exon junction (that is, more than ~25–30 nt upstream of an EJC), then NMD will occur. UPF1, together with SMG1, is thought to bind EJC-associated UPF2 in a way that is promoted by CBP80 (not shown). UPF1 binding to the EJC triggers UPF1 phosphorylation and NMD by promoting translational repression and recruiting mRNA degradative activities. Not shown are SMG5, SMG6 and SMG7, which seem to recruit protein phosphatase 2A (PP2A) and function in UPF1 dephosphorylation and, thus, recycling. AUG, translation initiation codon; STOP, normal termination codon.