Figure 1.
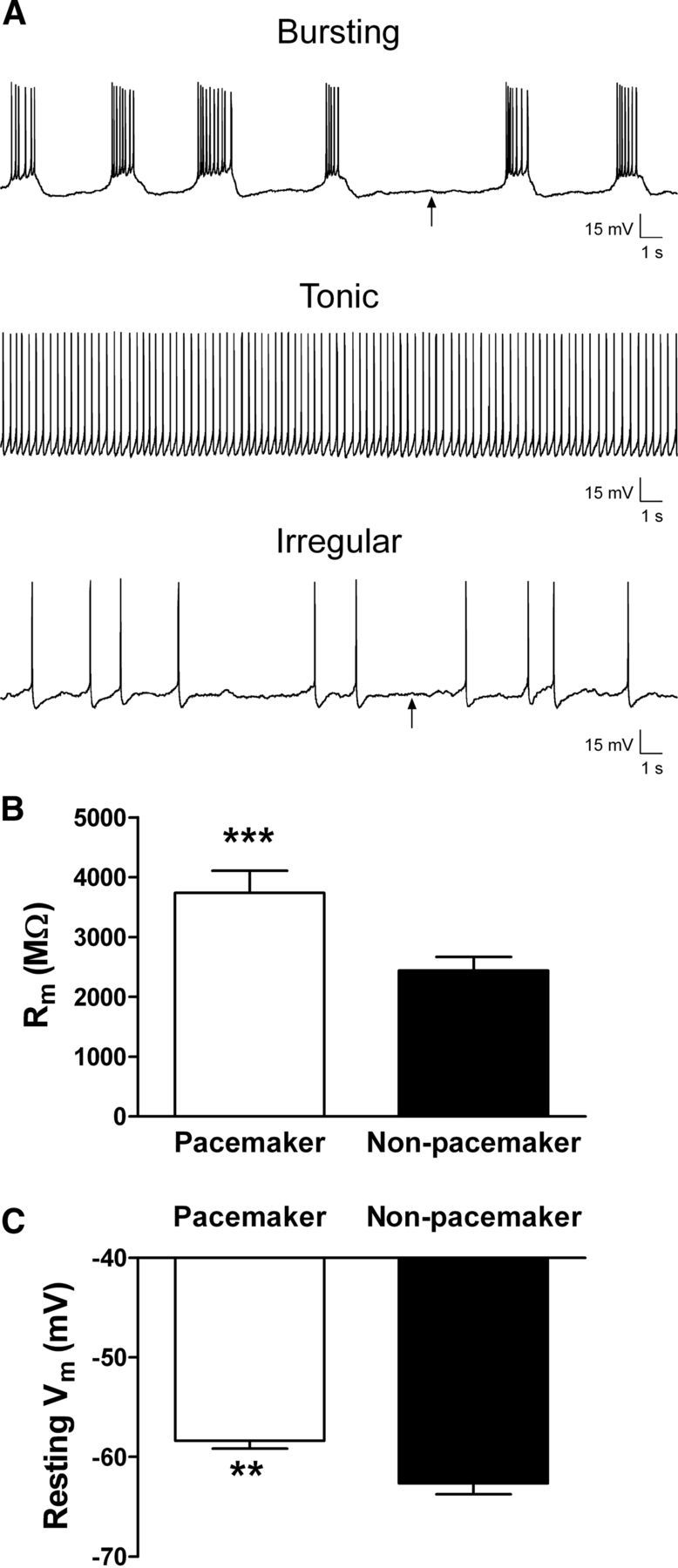
Lamina I pacemaker neurons are distinguished by high membrane resistance and depolarized resting potentials. A, Spontaneous firing patterns were classified as rhythmic bursting (top), tonic (middle), irregular (bottom), or silent (data not shown). Arrows indicate approximate regions used to measure the resting membrane potential in a spontaneously active neuron. B, Membrane resistance (Rm) was significantly higher in the pacemaker population of lamina I neurons compared with adjacent nonbursting neurons (***p = 0.0001, Mann–Whitney test). C, Pacemaker neurons also exhibited a significantly more depolarized resting potential (n = 15) compared with nonpacemaker neurons (n = 22; **p = 0.007, Mann–Whitney test). Tonically firing neurons were excluded from the analysis because of difficulties in accurately measuring their resting potential.
