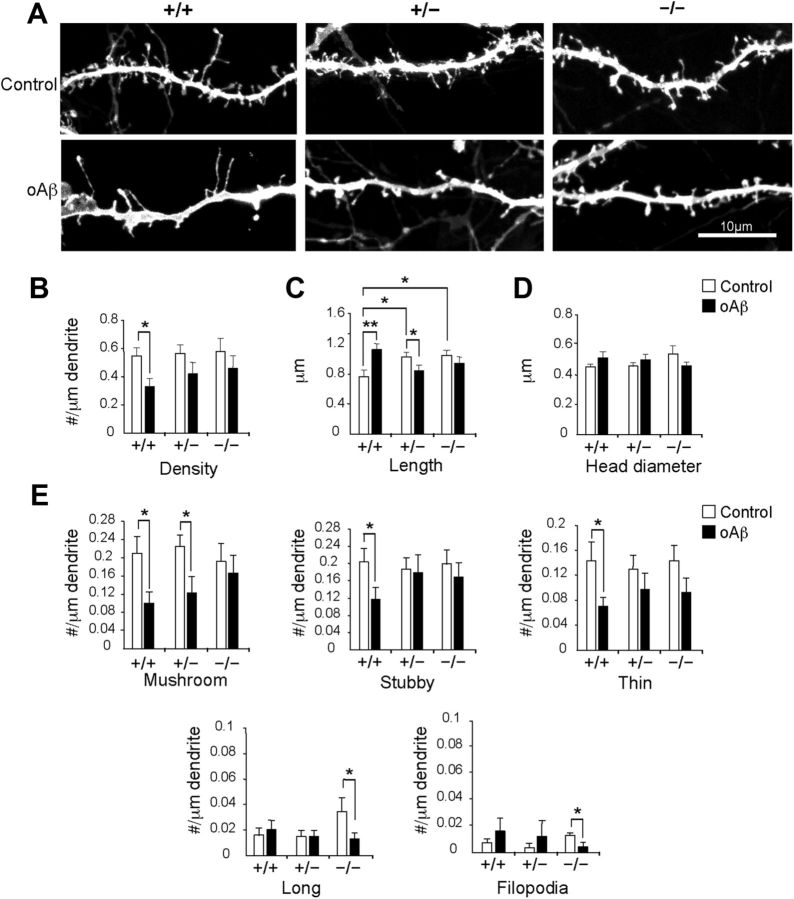
Figure 3.
Alterations of spine morphology attributed to Aβ are ameliorated with reduction of Synj1. A, Dendritic spines in hippocampal neuronal neurons exposed to 200 nm Aβ oligomer (oAβ) for 24 h and DiOlistically labeled from WT (+/+) cultures (n = 4): DMSO treated (n = 22) and oAβ treated (n = 21) neurons; Synj1+/− (+/−) cultures (n = 4): DMSO treated (n = 22) and oAβ treated (n = 20) neurons; or Synj1−/− (−/−) cultures (n = 3): DMSO treated (n = 19) and oAβ treated (n = 19) neurons. Scale bar, 10 μm. B, Spine density. C, Spine length. D, Spine head diameter. E, Spine class analysis using Neuron Studio, which distinguishes spine classes on the basis of length and presence of a spine head. Mushroom, stubby, and thin spines are <2 μm, while long spines and filopodia are >2 μm long. Mushroom and long spines have a head, while the other classes do not. The total number of spines analyzed was 3745 for 7415 μm length of dendrite as follows: Synj1+/+ (DMSO: 758; oAβ: 414); Synj1+/− (DMSO: 722; oAβ: 408); Synj1−/− (DMSO: 686; Aβ: 757).