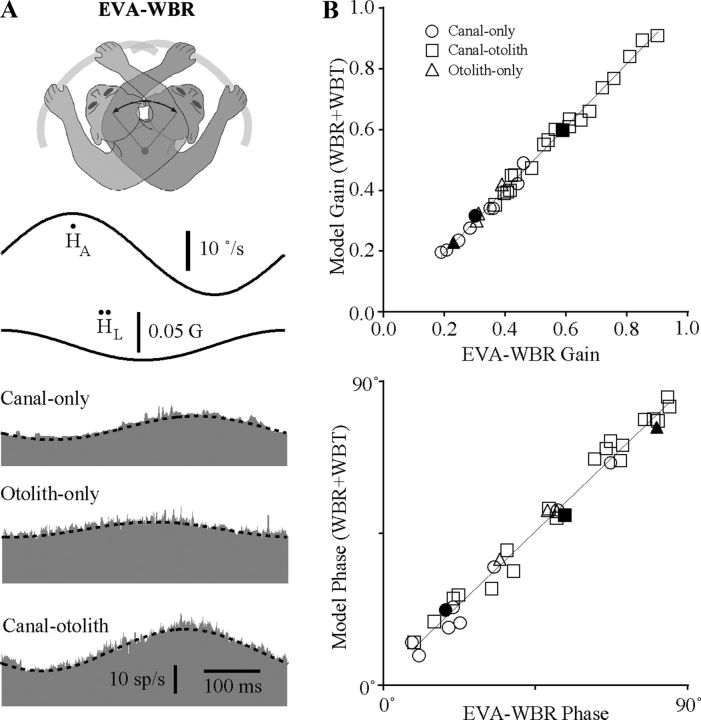
Figure 4.
A, Responses during eccentric off-axis rotations (EVA-WBR). The three neurons illustrated are the same as those in Figure 3. Responses are shown for EVA-WBR (2 Hz, ±10°/s) while the head was located 8 cm in front of the earth-vertical axis. Each row corresponds to a different type of unit including a canal-only neuron, an otolith-only neuron, and a canal–otolith neuron. Traces shown include head velocity (Ḣ), head acceleration (Ḧ), and unit discharge rate (gray fill). Schematic illustration at the top shows the paradigm that was used. Models superimposed on each unit's response (dashed lines) are a linear combination of the WBR and WBT response sensitivities illustrated in Figure 3 (see Materials and Methods). All recordings were from animal B. All averages included 30 stimulus cycles. B, Linearity of responses during eccentric off-axis rotations (EVA-WBR). Top, Estimated gain from a linear model representing a combination of the WBR and WBT response sensitivities as a function of the gain determined by regressively fitting the neural response. The superimposed line is a linear fit (model gain = 1.04*geva-wbr− 0.041sp/s/°/s; R2 = 0.993). Bottom, Estimated response phase from the linear model as a function of the response phase determined by regressively fitting the neural response. The superimposed line is a linear fit (model phase = 0.96*θeva-wbr + 2.9°; R2 = 0.984). Thirty-two neurons are shown including: 9 canal-only, 4 otolith-only, and 19 canal–otolith neurons (see legend). The filled symbols are the three neurons illustrated in Figure 3.