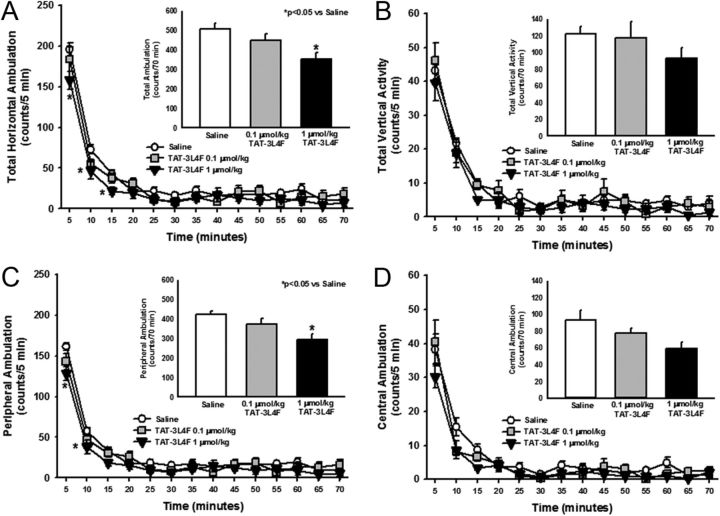
Figure 5.
The TAT–3L4F peptide suppresses ambulation but not vertical activity. We assessed the effects of saline (1 ml/kg, i.p.) or rat TAT–3L4F peptide (0.1 or 1 μmol/kg, i.p.) on spontaneous locomotor activity. A, The time course of horizontal ambulation is divided into 5 min time bins across the 70 min session; TAT–3L4F at 1 μmol/kg significantly reduced horizontal ambulation versus saline during the first 15 min. A, Inset, The mean ± SEM total horizontal ambulation is represented after administration of saline or TAT–3L4F; TAT–3L4F (1 μmol/kg) significantly reduced total horizontal ambulation versus saline. B, The time course of vertical activity is divided into 5 min time bins across the 70 min session. B, Inset, the mean ± SEM total vertical activity is represented after administration of saline or TAT–3L4F. C, The time course of peripheral ambulation is divided into 5 min time bins across the 70 min session; TAT–3L4F (1 μmol/kg) significantly reduced peripheral ambulation versus saline during the first 10 min. C, Inset, The mean ± SEM total peripheral ambulation is represented after administration of saline or TAT–3L4F; TAT–3L4F (1 μmol/kg) significantly reduced peripheral ambulation versus saline. D, The time course of central ambulation is divided into 5 min time bins across the 70 min session. D, Inset, The mean ± SEM total central ambulation is represented after administration of saline or TAT–3L4F. *p < 0.05 versus saline.