Figure 4.
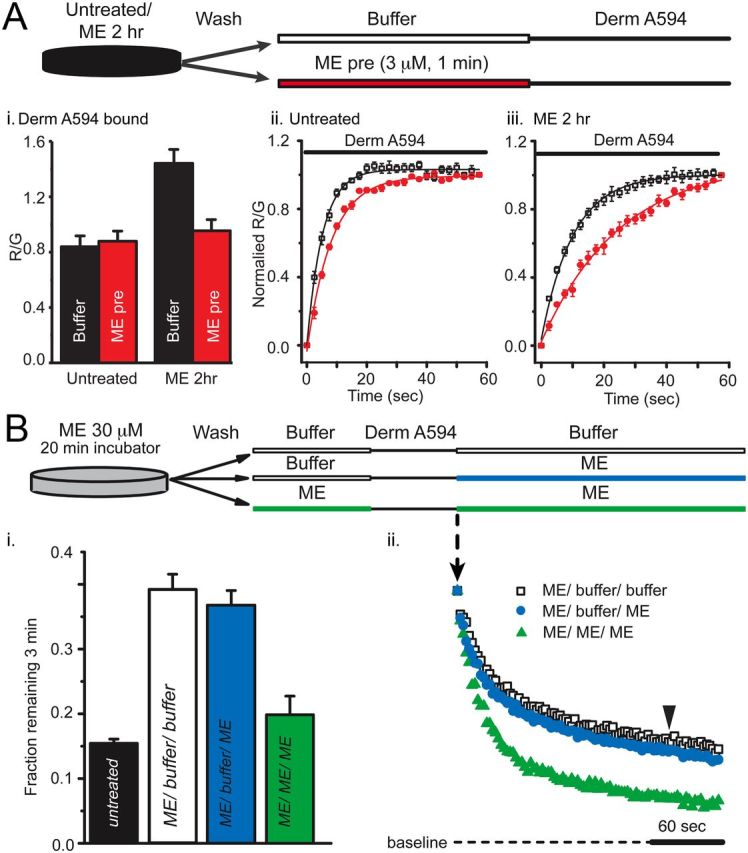
ME unbinds slowly after prolonged ME treatment. A, The amount of derm A594 bound relative to M1 A488 was measured in cells either untreated (Aii) or treated with ME (30 μm, 2 h) (Aiii). After treatment (untreated or ME 2 h), cells were washed with buffer and then subjected to a short pulse of buffer (black) or ME (3 μm, 60 s, red) immediately preceding derm A594 application (200 nm, 60 s) as diagrammed. Ai, Binding of derm A594 was imaged, and the relative amount of derm A594 bound after 60 s (R/G) was measured and plotted the average normalized amount of derm A594 that bound is plotted. Aii, Aiii, Binding of derm A594 (200 nm) is plotted as a function of time in untreated (Aii) or ME (30 μm, 2 h) treated cells (Aiii) and prepulsed with either buffer (black) or ME (3 μm, 60 s, red); n = 5 or 6 each. B, derm A594 (100 nm, 60 s) was applied to cells that had been treated with ME (30 μm, 20 min) and washed with buffer (see diagram). Unbinding of derm A594 was monitored while washing with either buffer (ME/buffer/buffer, □) or ME (3 μm, ME/buffer/ME, blue). ME (3 μm, 1 min) was also pulsed both immediately before and after derm A594 binding to cells that were modulated by ME (30 μm, 20 min) to determine whether residual ME had an effect on derm A594 unbinding kinetics (green, ME/ME/ME). Averaged data in Bi show fraction of derm A594 remaining 3 min after washout (n = 7–11, indicated by arrowhead in Bii), and individual examples of derm A594 unbinding under each condition are shown in Bii.
