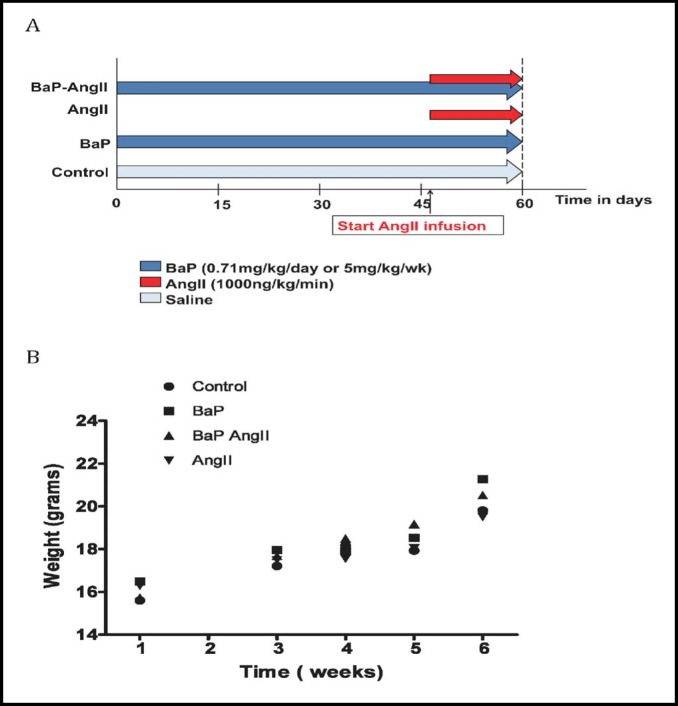
Fig. 1.
Study group assignment and assessment of normal development. A) Mice were evaluated in 4 groups in 2 study arms: BaP, AngII, BaP+AngII, and control. Exposure to BaP was via oral gavages and AngII exposure via subcutaneous osmotic mini pumps. In the BaP+AngII group, AngII infusion overlapped the last two weeks of BaP treatment. In the first study arm, mice were exposed to 5mg/kg/week of BaP for 42 days, and in the second arm 0.71mg/kg daily for 60 days (Figure only illustrates 60-day marker for the first study arm). B) Assessment of normal development. During the duration of the study, body weight was used as an indirect measure of exposure toxicity (failure to thrive). Incremental weight gain during the study period suggests normal growth. No statistically significant differences were observed between groups. Graph was derived from the weekly-exposure study arm (5 mg/kg/week of BaP); similar findings were noted in the daily-exposure arm (0.71 mg/kg/day) (data not shown).