Fig. 1.
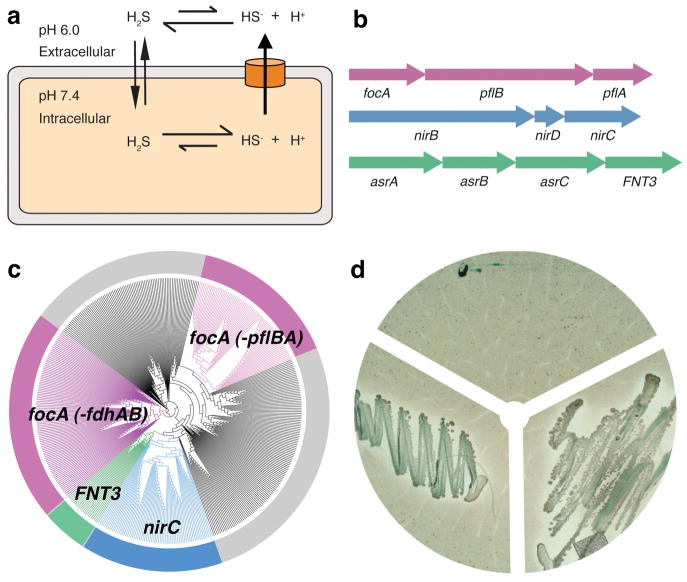
Genetic analyses and functional characterization of the FNT3/HSC gene and the asrABC operon. a, Model of the intracellular anion concentrative effect for the weak acid H2S. b, Genomic organization of FNT and their metabolically related reductase genes. Representatives are shown for the focA, nirC and FNT3/HSC genes with their respectively linked operons. c, Phylogentic tree of 474 bacterial and archaeal members of the FNT family. Branches are colorized based on genetic linkage to metabolic enzymes: pyruvate formate lyase (pflAB) or formate dehydrogenase (fdhAB) linked genes are colored pink, nitrite reductase (nirBD) linked genes are colored blue, and sulfite reductase linked genes (asrABC) are colored green. The FocA protein in archaea is encoded by the fdhC gene. The gray areas represent FNT family members with no assigned function based on genetic linkage. d, Bismuth sulfite agar plate assay. Top: vector control, left: asrA, asrB, asrC, right: asrA, asrB, asrC, FNT3.