FIG. 7.
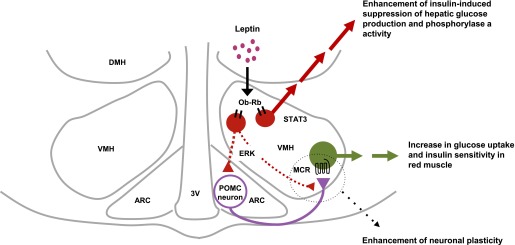
Model for the mechanism of regulation of glucose metabolism in muscle and liver by leptin in the VMH. Ob-Rb in the VMH plays a key role in the regulation of glucose metabolism and insulin sensitivity in muscle and liver by leptin. Leptin-activated MEK-ERK signaling in the VMH increases insulin sensitivity and glucose utilization in red muscle through activation of MCR in the VMH. Ob-Rb–expressing VMH neurons likely activate POMC neurons either in the ARC itself (14) or at their synaptic connections with VMH neurons through the MEK-ERK pathway. The MEK-ERK pathway then stimulates synaptic plasticity for POMC neurons and MCR-expressing neurons in the VMH. Whereas other brain sites may contribute to the leptin-induced enhancement of the suppressive effect of insulin on hepatic glucose production, leptin-activated STAT3 signaling in the VMH mediates this enhancement by inhibiting glycogen phosphorylase a activity in liver. 3V, third ventricle.
