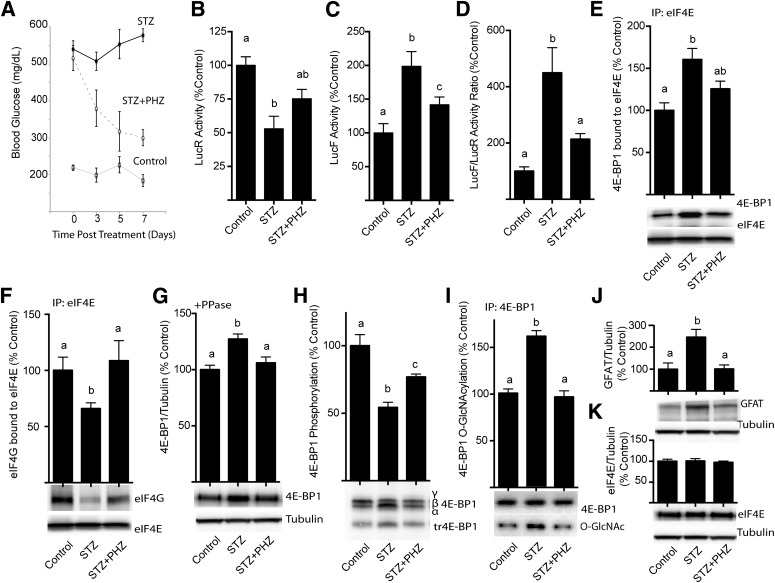
FIG. 2.
Phlorizin lowers blood glucose concentrations in STZ-treated mice and represses the diabetes-induced shift from cap-dependent to cap-independent translation in liver. Diabetes was induced in transgenic mice by STZ injection. Four weeks after the induction of diabetes, control and STZ mice were subcutaneously injected with solvent or phlorizin (PHZ) twice daily for 7 days to lower blood glucose concentrations (A). B and C: Luciferase activity was assessed in 1,000g supernatant fractions from liver extracts. Translation of LucR is under control of the cytomegalovirus (CMV) promoter in a cap-dependent manner, and LucF is regulated by the FGF-2 IRES. D: Ratio of LucF to LucR activity in liver supernatant fraction. The interaction of 4E-BP1 (E) and eIF4G (F) with eIF4E was examined by immunoprecipitating eIF4E and measuring the amount of each protein in the immunoprecipitate (IP) by Western blot analysis. G: 4E-BP1 content was measured by treating the supernatant fraction with λ-phosphatase (PPase) followed by Western blot analysis as previously described (11). H: Phosphorylation of 4E-BP1 was assessed as the ratio of the protein in the hyperphosphorylated γ-isoform to the total amount of 4E-BP1 in all isoforms. I: O-GlcNAcylation of 4E-BP1 was assessed by immunoprecipitating 4E-BP1 and measuring the amount of O-GlcNAcylation (O-GlcNAc) by Western blot relative to the total amount of 4E-BP1. Total content of GFAT (J) and eIF4E (K) was assessed by Western blot analysis. Values are means ± SE for two independent experiments (n = 8). Statistical significance was assessed by ANOVA followed by Holm-Sidak multiple-comparisons test to compare the mean of each group with the mean of every other group. Statistical significance is denoted by the presence of different letters above the bars on the graphs. Bars with different letters are statistically different; P < 0.05.