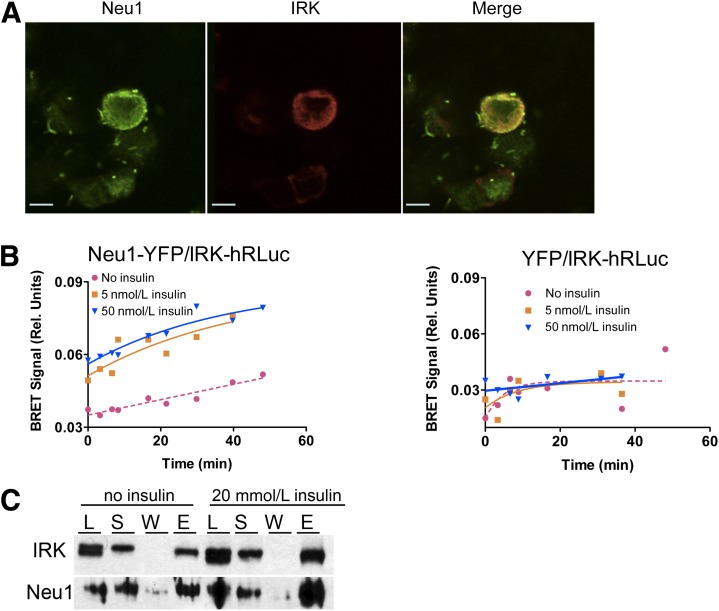
FIG. 4.
Insulin-induced interaction between IRK and Neu1 on the cell surface. A: Colocalization of IRK and Neu1 on the plasma membrane. HEK cells expressing Neu1-YFP and IRK-hRluc chimeric proteins were fixed with paraformaldehyde, permeabilized by Triton X-100, and costained with mouse anti-insulin receptor β-chain (Cell Signaling) (1:400) and rabbit anti-Neu1 (1:100) antibodies. Cells were then counterstained with Oregon Green 488–conjugated anti-rabbit IgG antibodies and Texas Red–conjugated goat anti-mouse antibodies (1:1,000; Molecular Probes). Slides were studied on a Zeiss LSM510 inverted confocal microscope. B: Detection of interaction between IRK and Neu1 by BRET. HEK cells expressing Neu1-YFP and IRK-hRluc (left) or YFP and IRK-hRluc (right) were treated with coelenterazine H in the absence or in the presence of 5 and 50 nmol/L insulin, and the BRET signal was calculated as the ratio of light intensity emitted by IRK-hRluc (530 nm) and Neu1-YFP (480 nm). In the absence of insulin, only the background levels of energy transfer between Neu1-YFP and IRK-hRluc are observed, whereas incubation of cells with insulin at physiological concentration of 5 nmol/L results in the appearance of BRET signal. C: Coimmunoprecipitation of IRK and Neu1. Hek293T cells overexpressing IRK-hRluc, Neu1-YFP, and CathA plasmids were treated or not with 20 nmol/L insulin for 15 min, washed with ice-cold PBS, and lysed in RIPA buffer containing dithiobis(succinimidyl propionate) cross-linker. After removal of cell debris by centrifugation, supernatants were subjected to immunoprecipitation using anti-insulin receptor β-chain antibodies. Proteins in cell lysate (L), supernatant of cell extract (S), protein A agarose washes (W), and eluate (E) were analyzed by Western blotting using anti-insulin receptor β-chain and anti-Neu1 antibodies.