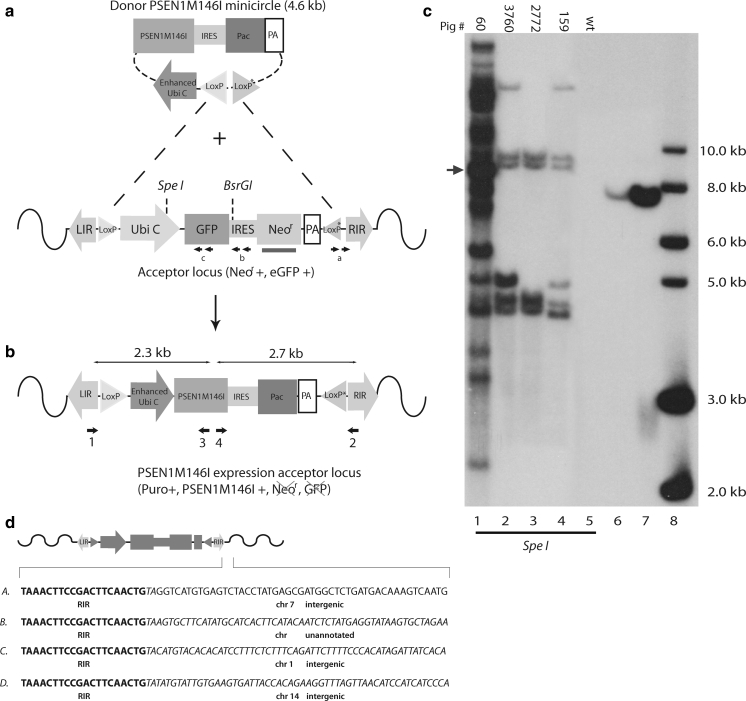
Fig. 1.
Establishment of Sleeping Beauty DNA transposon transgenic pigs for RMCE. a Schematic representation of Cre mediated RMCE in the pSBT/floxedUbi-GIN acceptor locus. The acceptor locus consists of a Sleeping Beauty DNA transposon with the GFP gene (green rectangle) linked to neomycin resistant gene (Neo r, grey rectangle) through an internal ribosomal entry site (IRES, light grey rectangle). This unit is controlled by the humane ubiquitin C promoter (Ubi C, light green arrow) and a SV40 polyadenylation signal (PA). Two incompatible loxP sites (yellow triangles; Asterisk indicates mutated loxP site) flank the cassette for RMCE. The transposon unit is demarcated by LIR and RIR (grey arrows). The RMCE donor minicircle is composed of a CMV enhanced Ubi C promoter (blue arrow) controlling the PSEN1M146I gene (orange rectangle) linked to the puromycin resistance gene, Pac (grey rectangle), through an IRES element (small grey rectangle). b Schematic representation of the acceptor locus after RMCE. Primers to verify RMCE are marked with small black arrows and the corresponding lengths of the PCR products marked by thin arrows. c Southern blot analysis of genomic DNA from SBT/floxedUbi-GIN–transgenic pigs and wt pig digested with SpeI (lanes 1–5). A 670-bp Neor fragment was used as probe (red rectangle in a). Pig identification numbers are shown above lanes. Lanes 6 and 7 include BamHI-digested pSBT/floxedUBi-GIN representing DNA amounts equivalent to one and twenty copies, respectively. Lane 8, DNA ladder. The blue arrow marks a putative concatemer d Junction site sequences identified by LDI-PCR in pig #2772 harboring four copies of SBT/floxedUBi-GIN (a, b, c, d). (Color figure online)