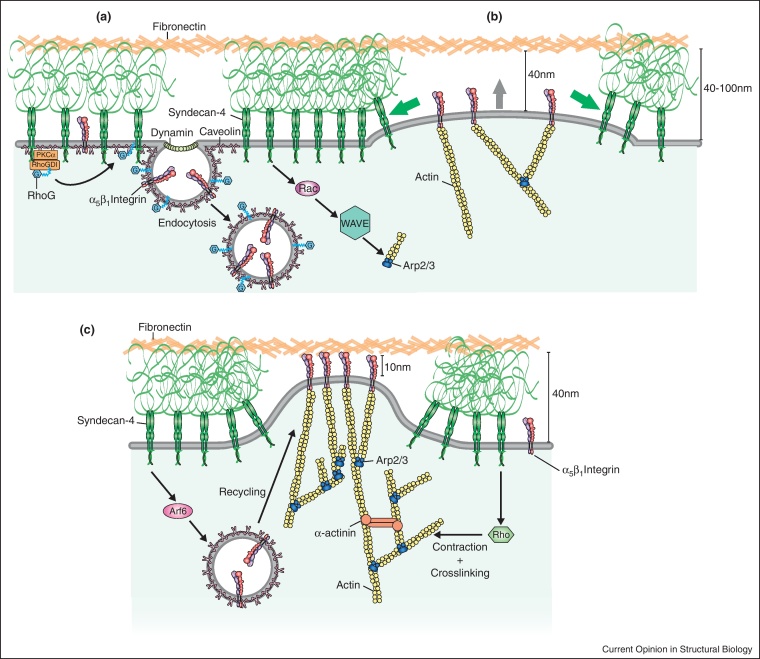
Figure 3.
Spatial rearrangement of syndecan and integrin during adhesion formation. (a) Syndecan-4 detects fibronectin that is greater than 40 nm from the plasma membrane and triggers RhoG/caveolin-dependent endocytosis of integrin and Rac1-dependent polymerisation of branched actin filaments. (b) Actin polymerisation causes local membrane protrusion that causes lateral movement of syndecan-4 due to spatial constraints as the gap between membrane and matrix decreases to 10–40 nm. (c) Once the plasma membrane is within 10 nm of the ECM, integrin engages fibronectin, forming a nouveau adhesion. Integrin is recycled through an Arf6-dependent pathway. Peripheral syndecan-4 activates RhoA to cause contraction and bundling of the actin cytoskeleton.