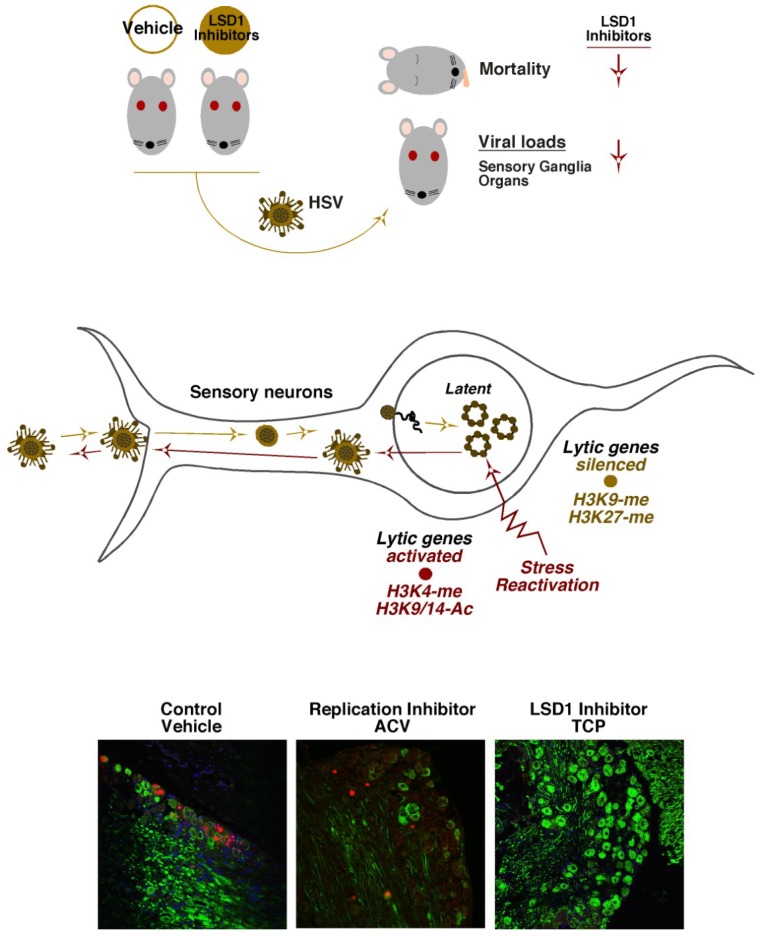
Figure 4.
Inhibitors of the HCF-1 associated histone demethylases reduce primary infection and block viral reactivation from latency. (Top Panel) Mice treated with either Vehicle control or LSD1 inhibitors were infected with HSV. Mortality and viral loads were assessed at defined time periods post infection. LSD1 inhibitors reduce mortality and viral loads relative to control. (Middle Panel) HSV infection of sensory neurons results in the establishment of latency in which lytic genes are repressed. Stress-mediated reactivation of viral infection results in conversion of repressive chromatin marks to activating marks on viral lytic genes. (Bottom Panel) Latently infected trigeminal ganglia were explanted into culture to induce viral reactivation in the presence of control vehicle, ACV (acycloguanosine, DNA replication inhibitor), or the LSD1 inhibitor, TCP (tranylcypromine). Ganglia were sectioned and stained for neurofilament (green) and the viral lytic replication protein UL29/ICP8 (red) to mark neurons undergoing productive reactivation.