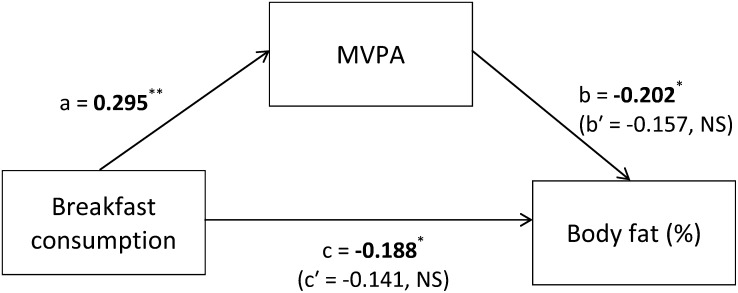
FIGURE 1.
Mediation model of the effect of MVPA on the association between breakfast consumption and percentage body fat. Values in boldface type represent standardized, age- and race-adjusted associations between breakfast consumption and MVPA (total effect, a), MVPA and percentage body fat (total effect, b), and breakfast consumption and percentage body fat (total effect, c). Values in parentheses represent standardized age- and race-adjusted associations between breakfast consumption and percentage body fat with control for the hypothesized mediator, MVPA (direct effect, c′), and between MVPA and percentage body fat with control for breakfast consumption (direct effect, b′). The indirect or mediation effect (ab′) was −0.046 and nonsignificant as assessed with the Sobel test: t = −1.48; 95% CI: −2.48, −0.12; P = 0.139. *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01. MVPA, moderate-to-vigorous-intensity physical activity.