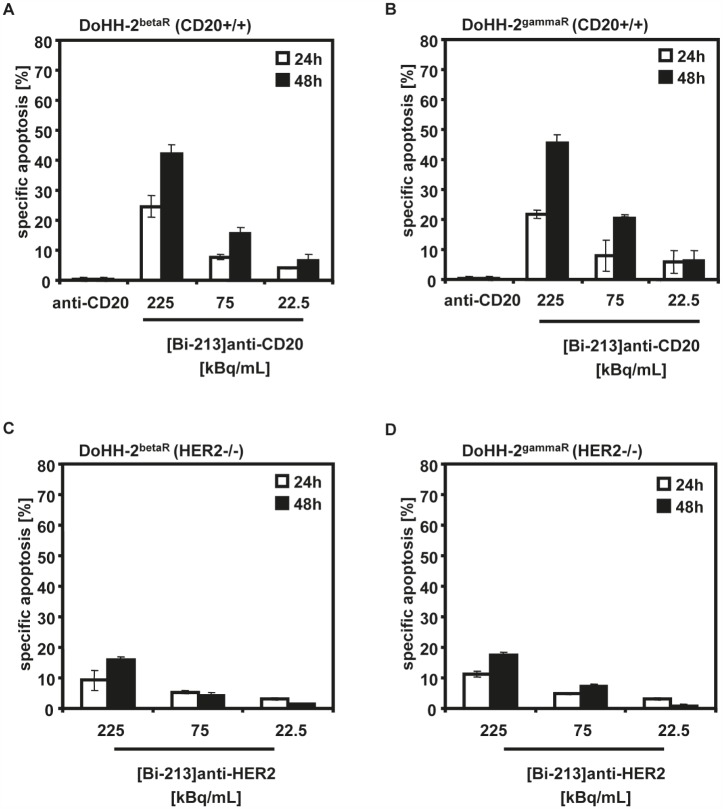
Figure 3. [Bi-213]anti-CD20 breaks radio- and chemoresistance in CD20-positive NHL cells.
(A,B) [Bi-213]anti-CD20 overcomes radio- and chemoresistance in CD20-positive (CD20+/+) beta-radiation resistant (DoHH-2betaR) (A) and gamma-radiation resistant DoHH-2 cells (DoHH-2gammaR) (B). DoHH-2 cells resistant against up to 5Gy Y-90 (DoHH-2betaR) (A) or resistant against up to 5Gy Cs-137 (DoHH-2gammaR) (B) and cross-resistant to different chemotherapeutics were incubated with different activity concentrations of [Bi-213]anti-CD20 as indicated or unlabelled anti-CD20 (anti-CD20), respectively. The amount of unlabelled anti-CD20 antibodies corresponds to the one used for the highest activity concentration of the radioimmunoconjugate [Bi-213]anti-CD20. (C,D) [Bi-213]anti-HER2 does not induce a strong cell death in HER2-negative (HER2−/−) DoHH-2betaR (C) or HER2-negative (HER2−/−) DoHH-2gammaR cells (D), respectively. DoHH-2betaR (C) or DoHH-2gammaR (D) were incubated with activity concentrations of [Bi-213]anti-HER2 as indicated. (A,B,C,D) After 24h (white columns) and 48h (black columns), the percentage of apoptotic cell death was measured by FSC/SSC-analysis. The specific cell death was calculated as described in Figure 2. Columns, mean of triplicates; bars, SD <10%.