Fig. 2. RNA-guided genome editing of the native AAVS1 locus in multiple cell types.
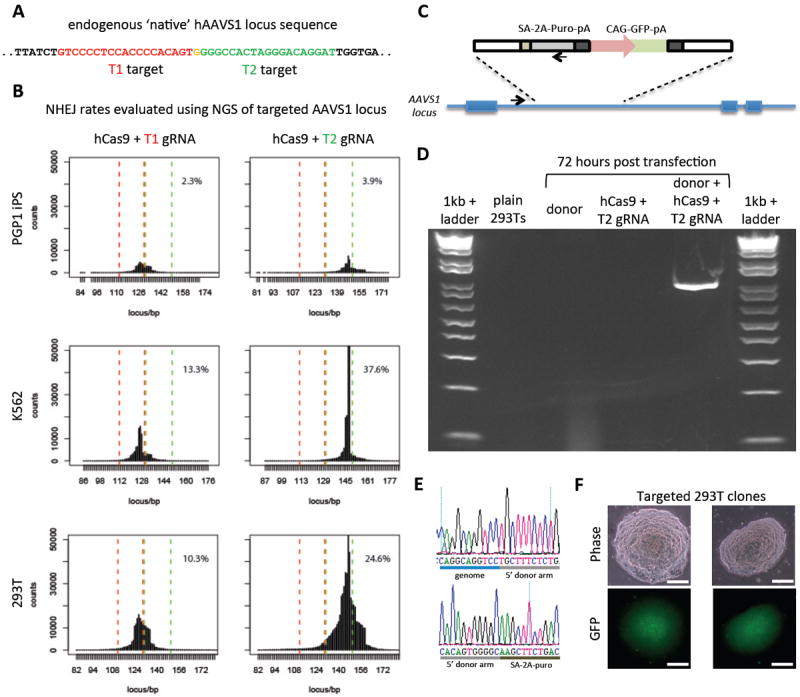
(A) T1 (red) and T2 (green) gRNAs target sequences in an intron of the PPP1R12C gene within the chromosome 19 AAVS1 locus. (B) Total count and location of deletions caused by NHEJ in 293Ts, K562s, and PGP1 iPS cells after expression of Cas9 and either T1 or T2 gRNAs as quantified by next-generation sequencing. Red and green dashed lines demarcate the boundaries of the T1 and T2 gRNA targeting sites. NHEJ frequencies for T1 and T2 gRNAs were 10% and 25% in 293T, 13% and 38% in K562, and 2% and 4% in PGP1 iPS cells, respectively. (C) DNA donor architecture for HR at the AAVS1 locus, and the locations of sequencing primers (arrows) for detecting successful targeted events, are depicted. (D) PCR assay 3 days after transfection demonstrates that only cells expressing the donor, Cas9 and T2 gRNA exhibit successful HR events. (E) Successful HR was confirmed by Sanger sequencing of the PCR amplicon, which showed that the expected DNA bases at both the genome-donor and donor-insert boundaries are present. (F) Successfully targeted clones of 293T cells were selected with puromycin for 2 weeks. Microscope images of two representative GFP+ clones is shown. (Scale bar, 100 μm.)
