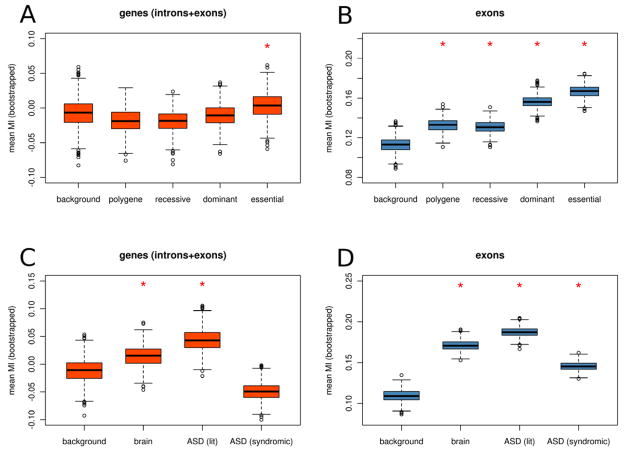
Figure 7. Disease genes are characterized by high mutability.
Disease genes are more mutable than non-disease genes (A) within genes and (B) within exons. In both cases, mutability is highest for genes involved in dominant disorders and mutability is increased to a lesser extent for genes involved recessive and polygenic traits. Mutability is significantly elevated for genes preferentially expressed in the brain (C- D) as well as genes involved in ASD (see methods for details). An asterisk indicates a significant difference compared to the respective background set (at α=0.01 by a two-sided t-test). See also Supplemental Table 3 and Supplemental Table 4 for the mean mutability index of exons and genes, respectively.