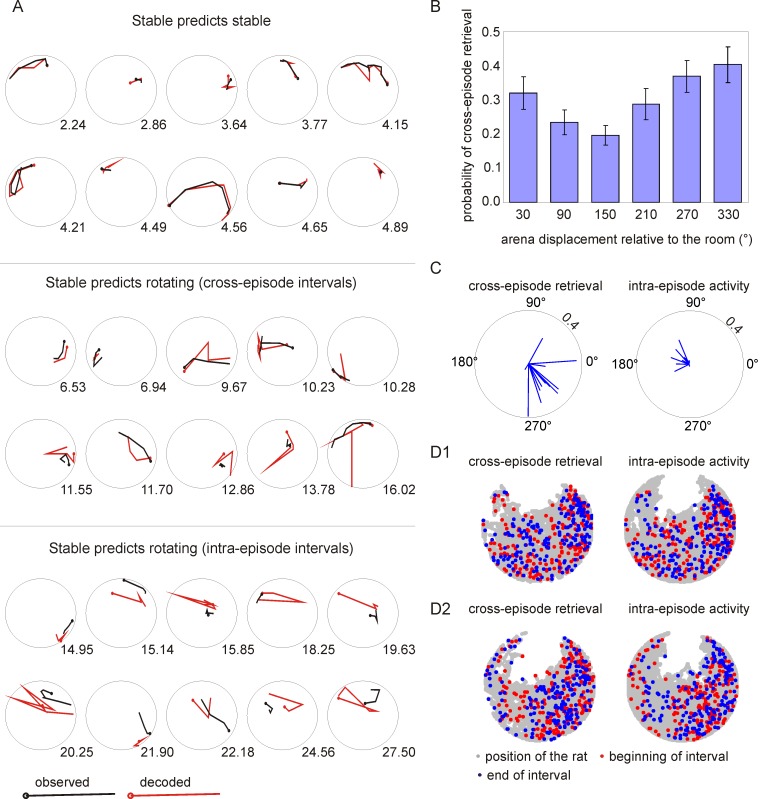
Figure 3. Influence of external cues on cross-episode retrieval.
(A) Examples comparing the ability to decode the rat's position during the stable and rotating conditions. The upper 10 plots display the 10 intervals with the best decoding during the stable condition. The middle 10 plots display the 10 cross-episode intervals with the best decoding. The bottom 10 plots display the 10 intra-episode intervals with the best decoding. In all cases the position was decoded using the spatial activity during the stable session as a template. The observed position of the rat is shown in black, the decoded position in red. The number next to each plot indicates the decoding error in cm. (B) The proportion of 1-s cross-episode intervals was computed for different angular displacements of the arena from its orientation in the stable condition. The probability of cross-episode retrieval was highest when the arena displacement was close to 0°—similar to the arena orientation in the stable condition. (C) The average arena displacement vectors are shown for each session during the cross-episode intervals and the intra-episode intervals. The distribution was not random in 11 out of 12 ensemble recording sessions (Raleigh's test, ps<0.005); cross-episode retrieval was most likely when the arena displacement within the room was between 270° and 360°. (D) The position of the rat during cross-episode intervals and intra-episode intervals is shown in the spatial frame of the room (D1) and the spatial frame of the arena (D2). Red and blue dots mark the beginnings and ends of the intervals. The data from a single session are shown.