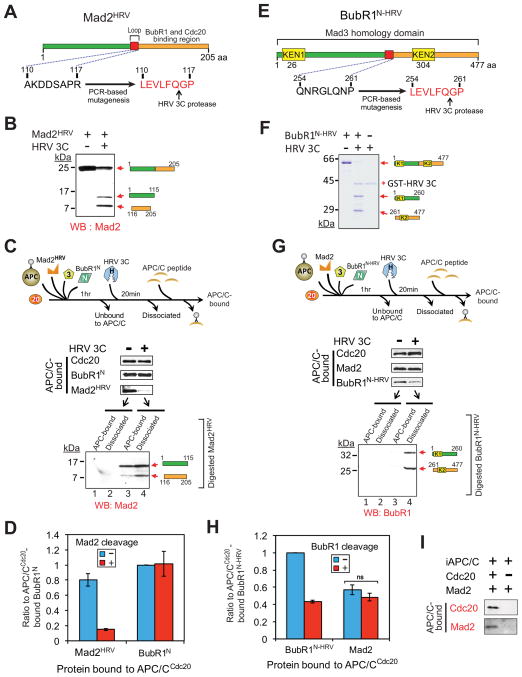
Figure 3. Maintaining the association of BubR1N with Cdc20 does not require the Mad2-Cdc20 interaction.
(A) Schematic of a Mad2 variant modified to contain a HRV 3C cleavage site. (B) Immunoblot showing HRV 3C-mediated cleavage of Mad2HRV in vitro. Mad2HRV was incubated at room temperature for 20 min in the presence or absence of HRV 3C protease. (C) After incubation with BubR1N, Bub3, Mad2HRV and Cdc20, APC/C was affinity-purified to remove unbound components. Following incubation with or without HRV 3C protease, dissociated components were washed away and APC/C was peptide-eluted from beads and analyzed for associated components by immunoblotting. The supernatant from the protease digestion mixture was collected and analyzed for release of the digested Mad2HRV fragments. (D) The amount of APC/C-bound BubR1N or Mad2HRV in (C) was measured. Values are plotted as the molar ratio of APC/C-bound Mad2HRV compared with APC/C-bound BubR1N. The level of APC/C-bound BubR1N without protease treatment was set to 1. Bars represent the mean. Error bars represent SEM (n=3). (E) Schematic of an HRV 3C cleavable variant of BubR1N. (F) HRV 3C-mediated digestion of the cleavable BubR1N in vitro. Cleavable BubR1N was incubated at room temperature for 20 min in the presence or absence of HRV 3C prior to analysis. (G–H) Effect of forced BubR1N release on the association of Mad2 with APC/CCdc20. (G) Experimental procedure is the same as in (C). (H) Values were plotted as the molar ratio compared with APC/C-bound BubR1N-HRV. The level of APC/C-bound cleavable BubR1N without the protease treatment was set to 1. Bars represent the mean. Error bars represent SEM (n=3). ***=P<0.0001. (I) Assay of Mad2 binding to APC/C in the presence and absence of Cdc20 (see also Fig. S3).